MPCVault Blog
MPCVault Blog
Product updates, security insights, and technical guidance
on MPC-based custody.
All (91)
Product update (60)
Assets (5)
Card (6)
Security (13)
App (25)
Developers (8)
Blogs (91)
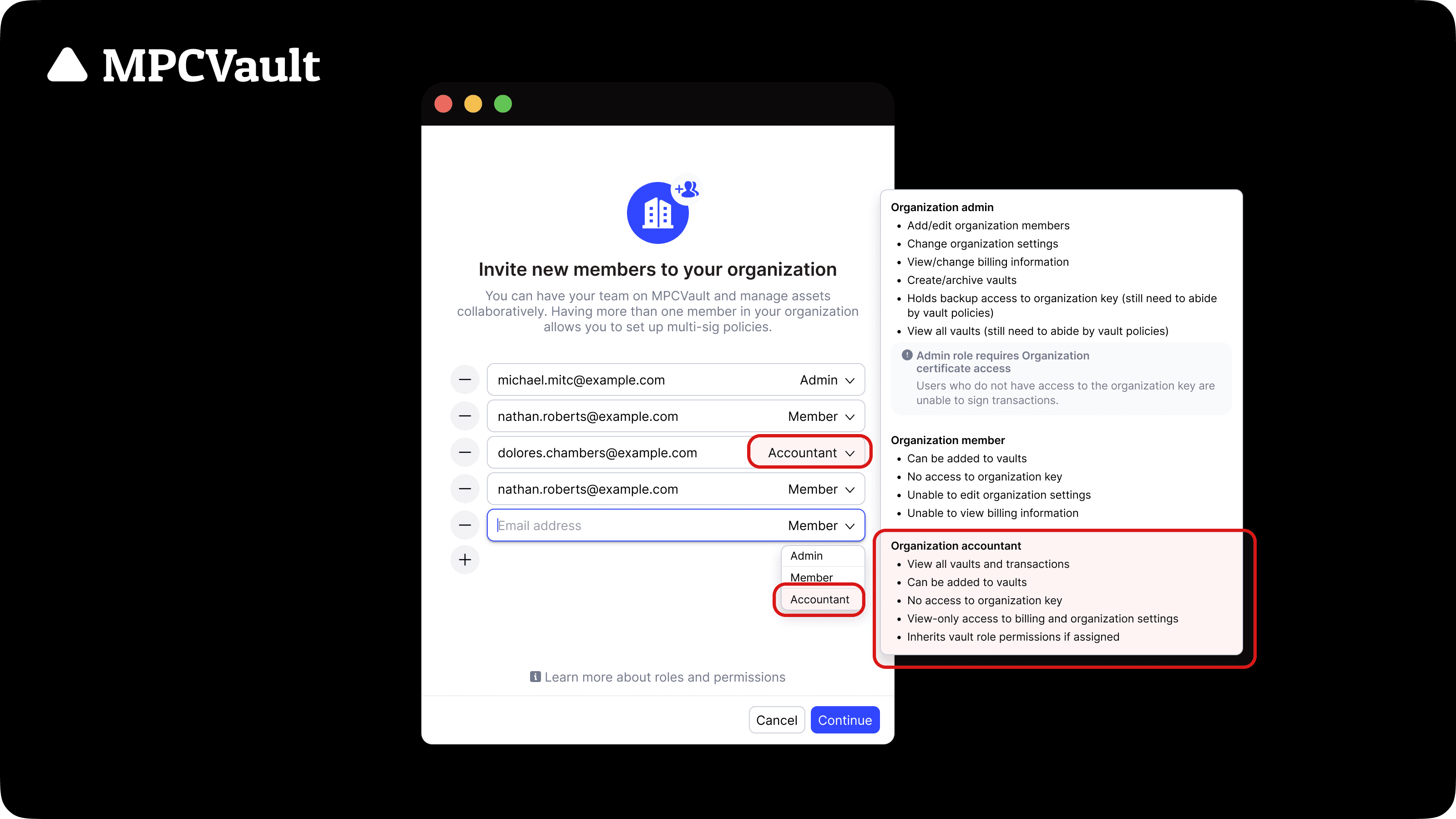
Product update, Organization accountant
Who introduced an accountant role to the organization

Julie
•
Nov 3, 2025
Read More
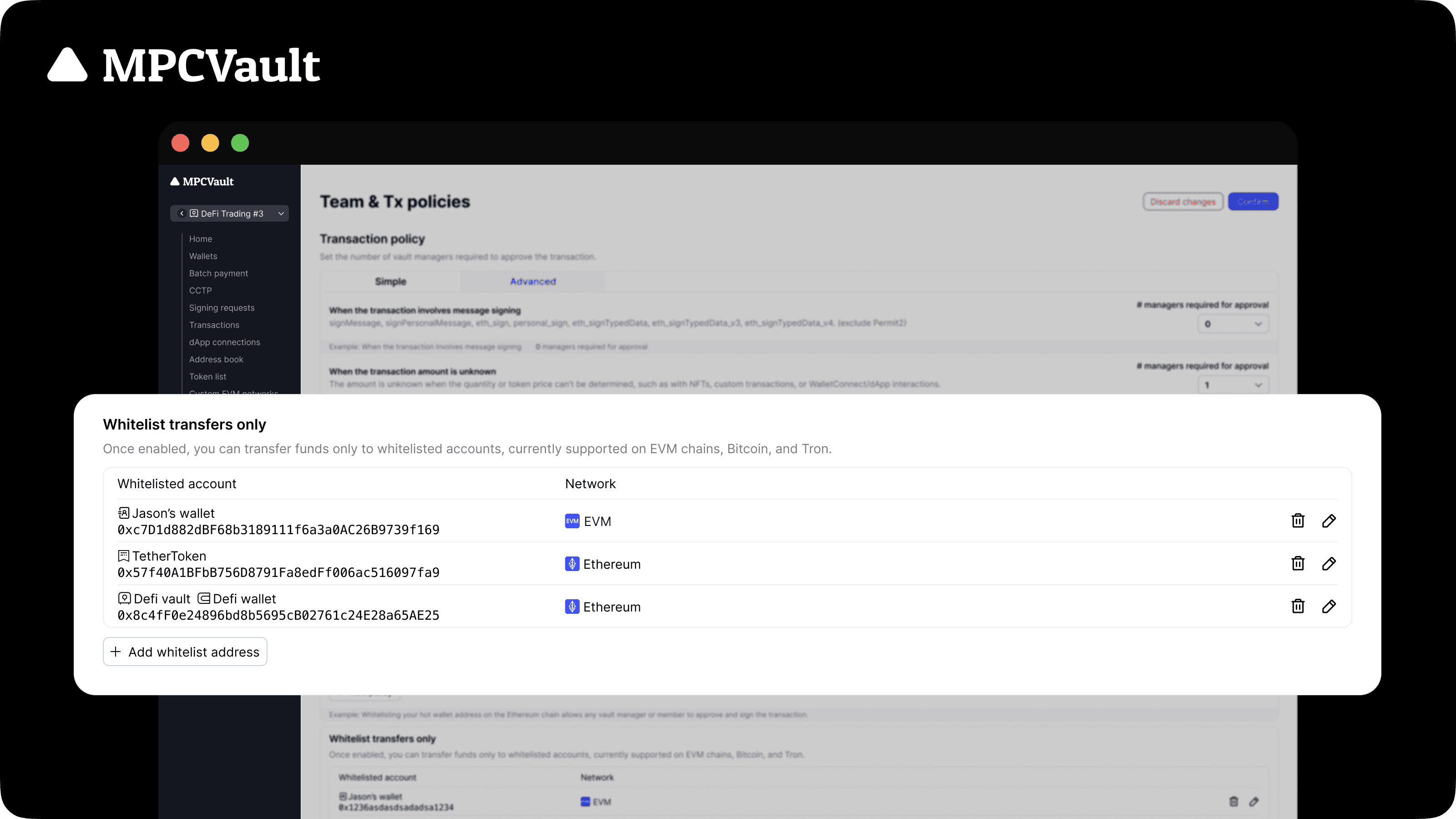
Product update, Transaction Policy, Whitelist Only Mode
Whitelist Transfers: restrict transactions to approved accounts

Julie
•
Nov 1, 2025
Read More
Product update, UI, App
The Liquid Glass effect is LIVE on iOS

Julie
•
Oct 27, 2025
Read More
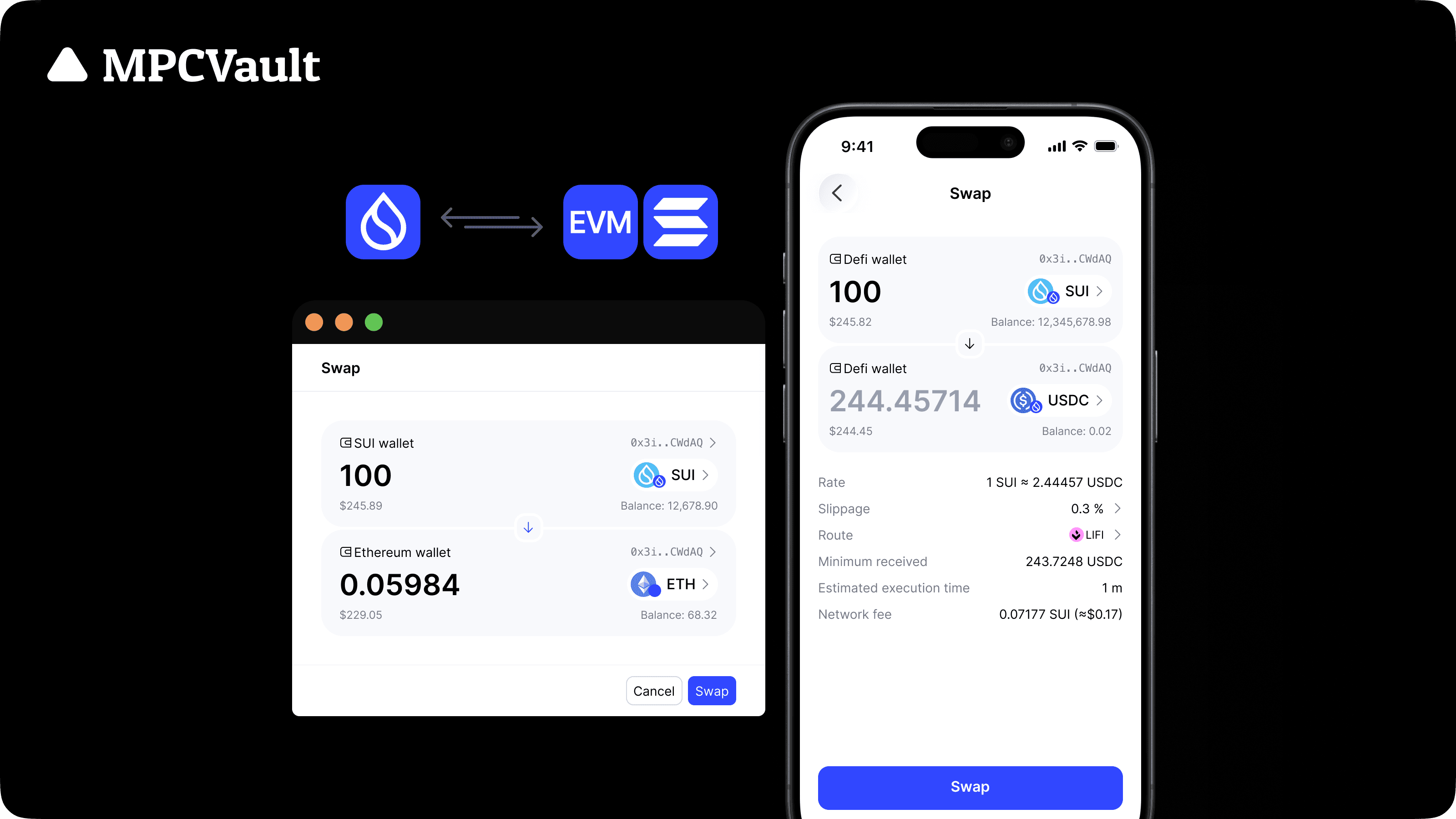
Product update, Sui, Swap
New Sui swap and cross-chain swap options

Julie
•
Oct 20, 2025
Read More

Product update, Card
Download card transaction history via CSV

Julie
•
Oct 13, 2025
Read More
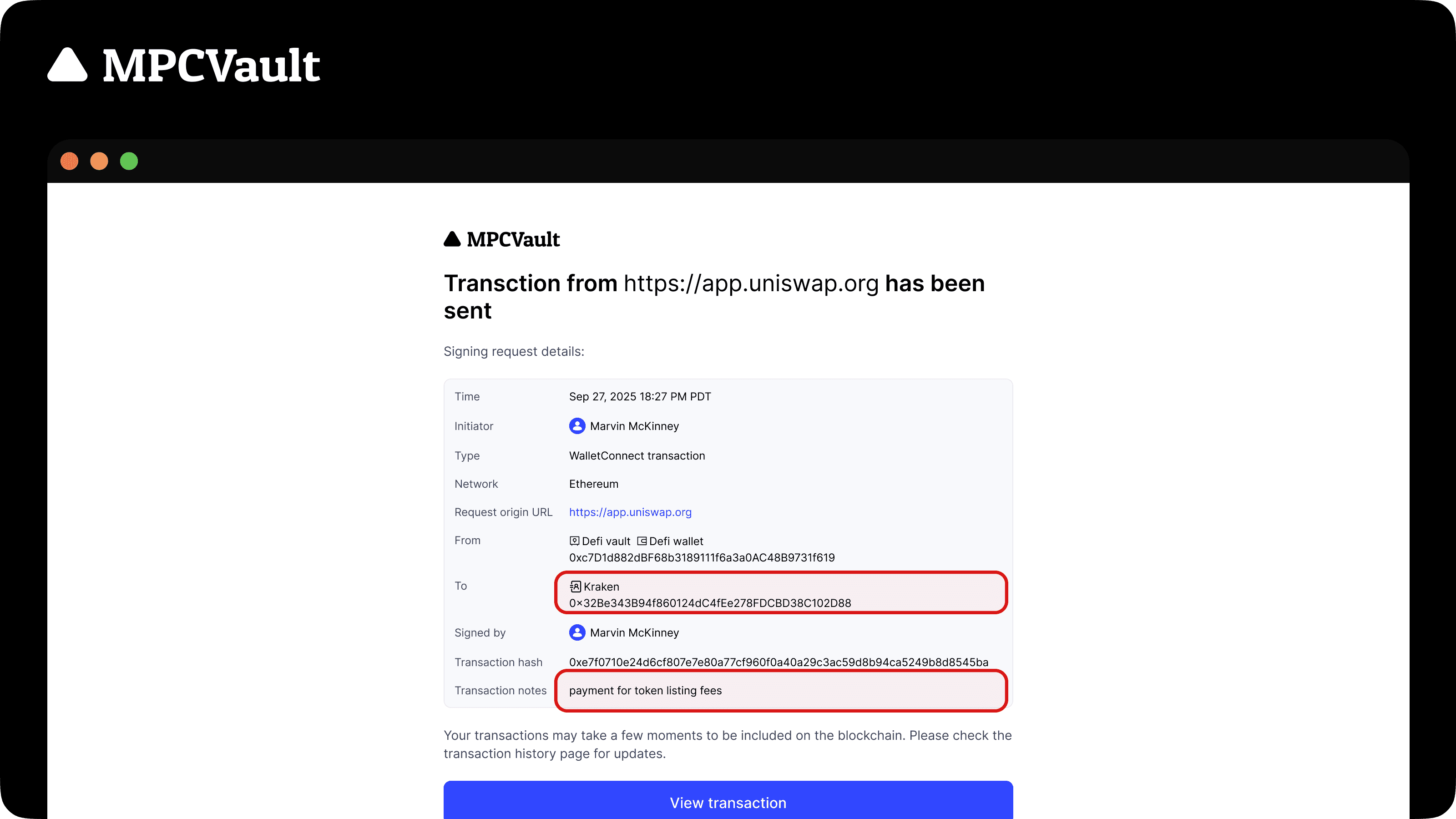
Product update, Email Notifications, Transaction Notes
Smarter email notifications: address book labels and transaction notes

Julie
•
Oct 9, 2025
Read More
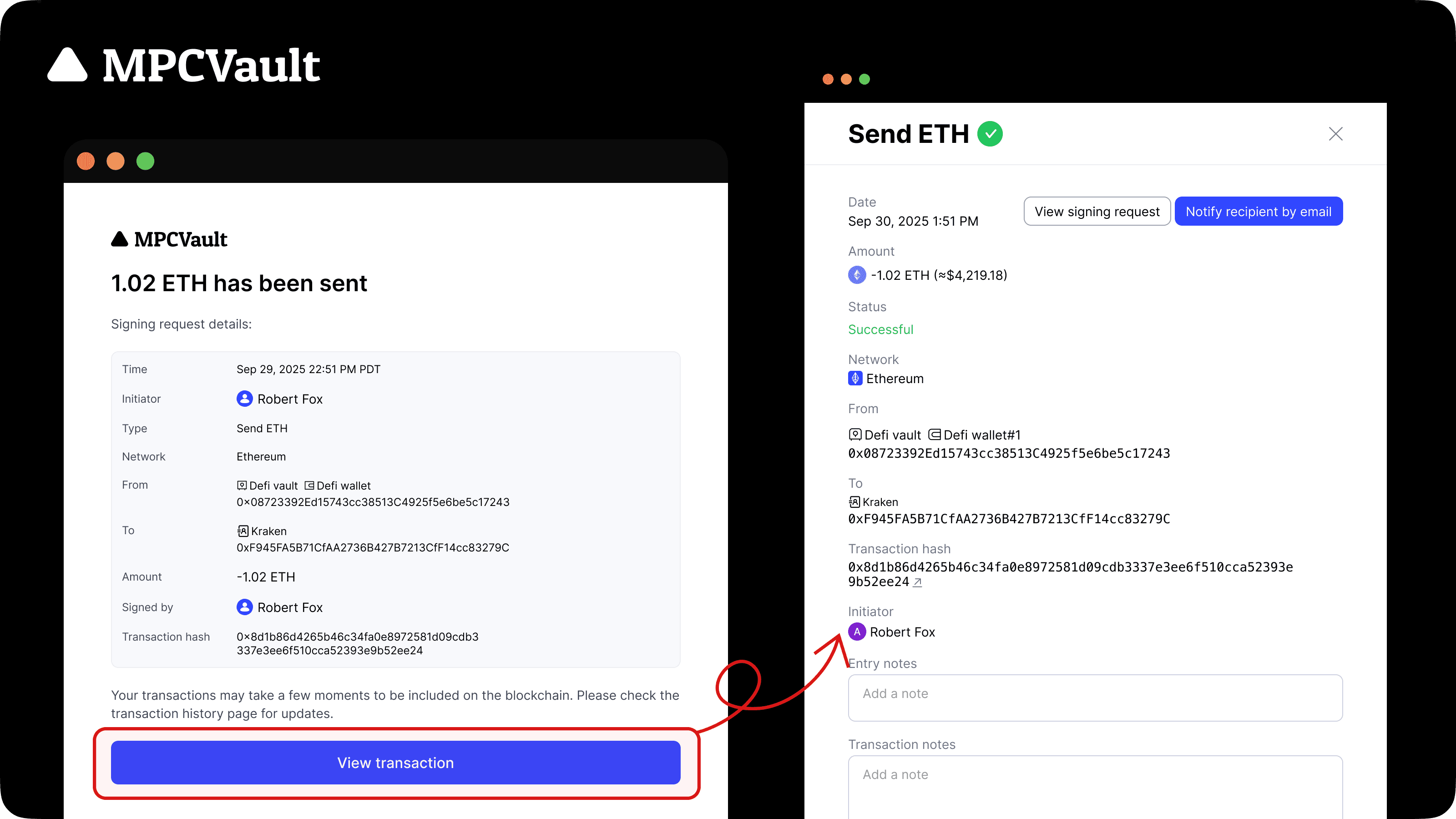
Product update, Email Notifications, UX
Direct link to transaction details from email

Julie
•
Oct 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, Off-ramp, USD
Expanded transfer type for US users

Julie
•
Sep 23, 2025
Read More
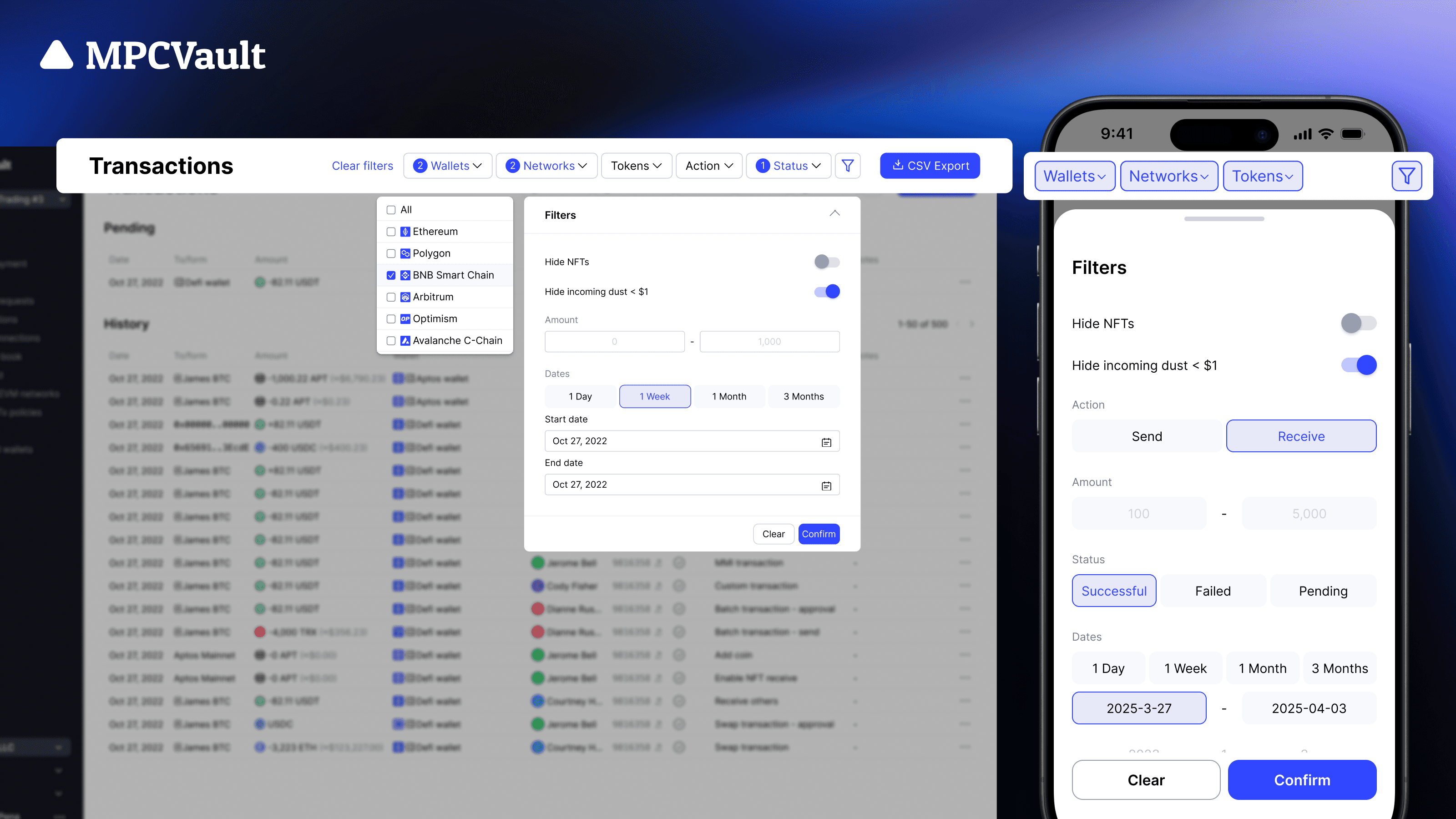
Product update, Transaction Filter, App, Web Console
The new transaction filter

Julie
•
Sep 19, 2025
Read More
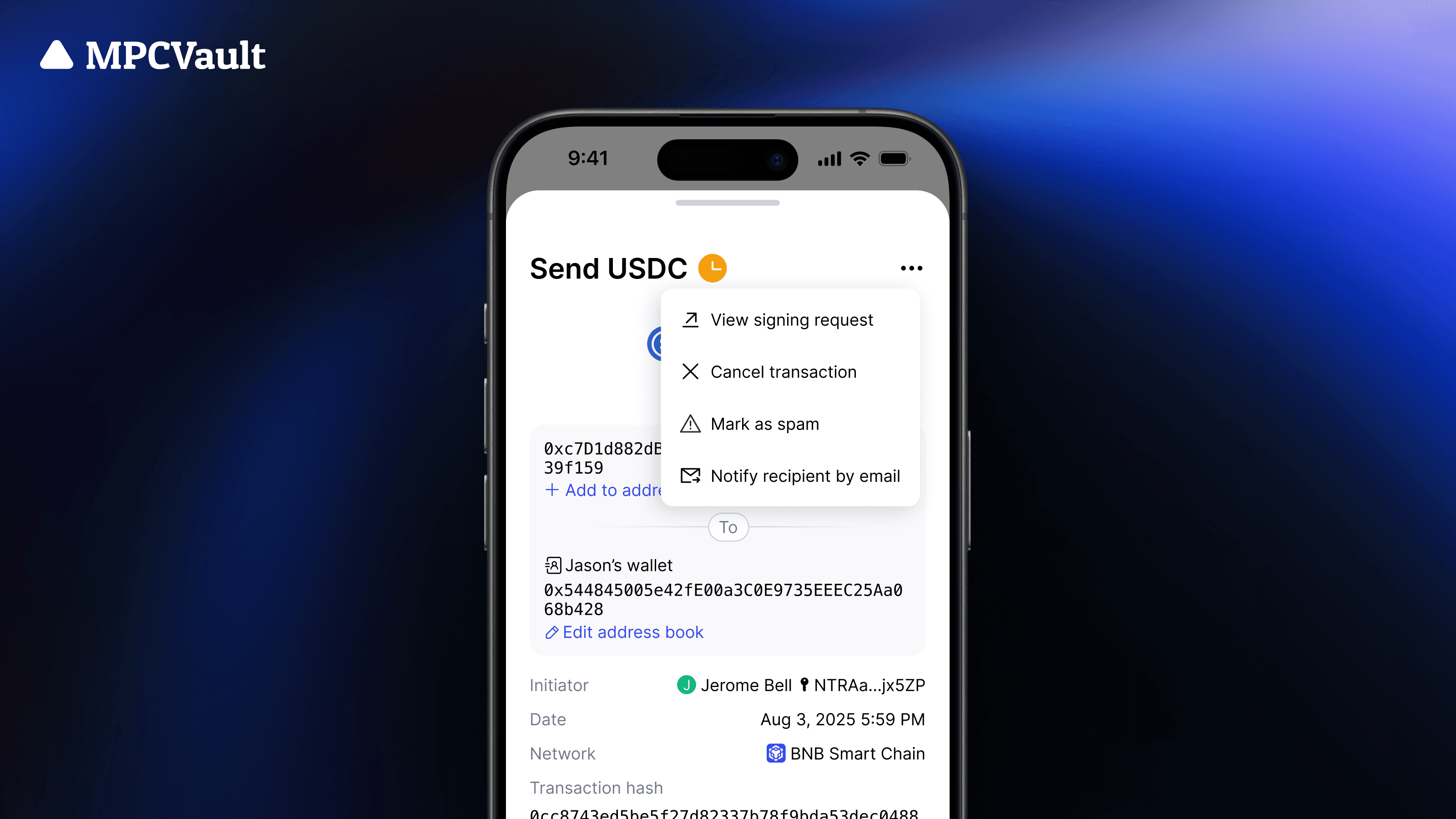
Product update, Assets, Mark As Spam, App
New menu in mobile app transaction details page

Julie
•
Sep 16, 2025
Read More
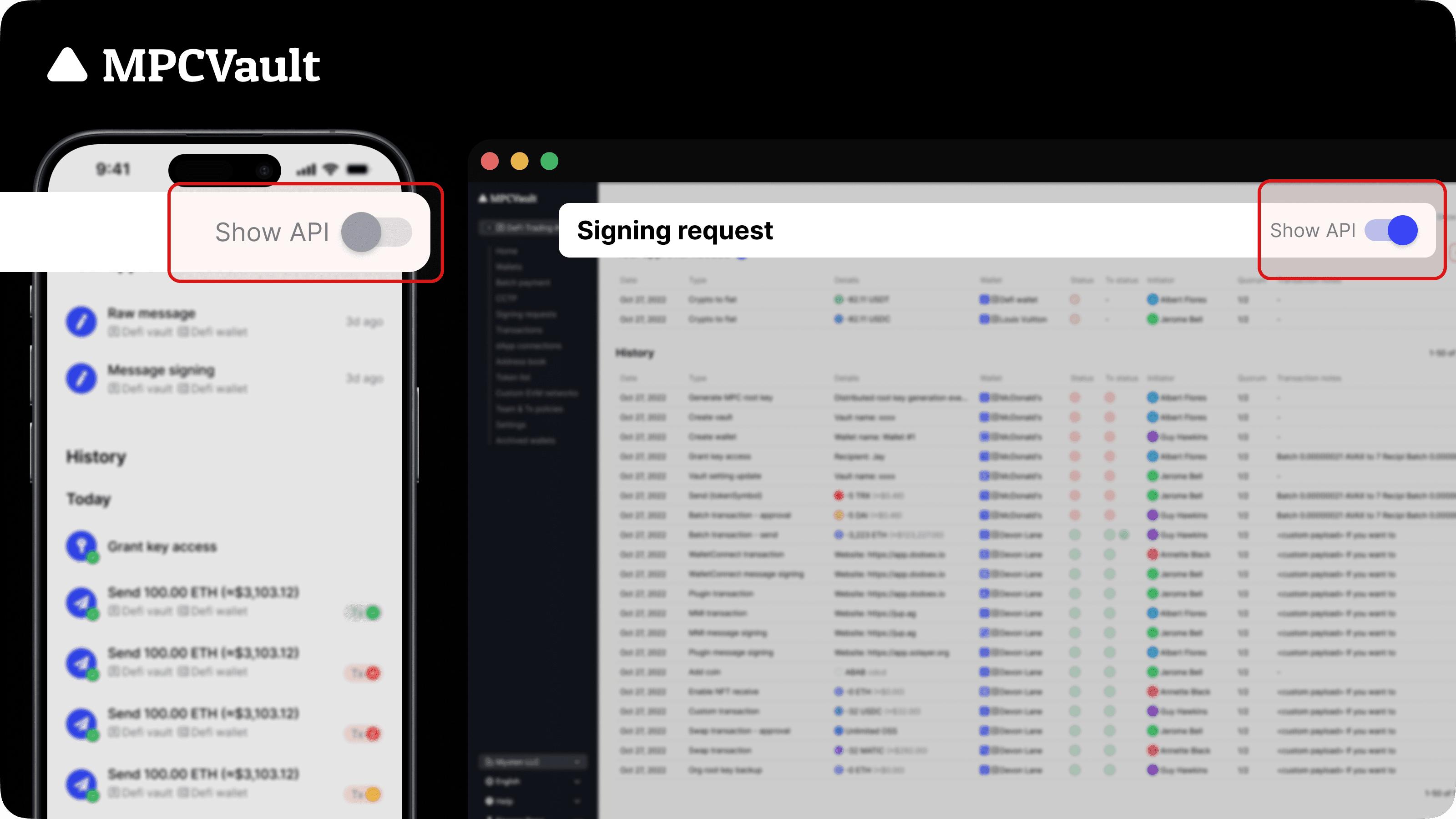
Product update, API, App, Web Console
Show API requests in the signing request list

Julie
•
Sep 12, 2025
Read More
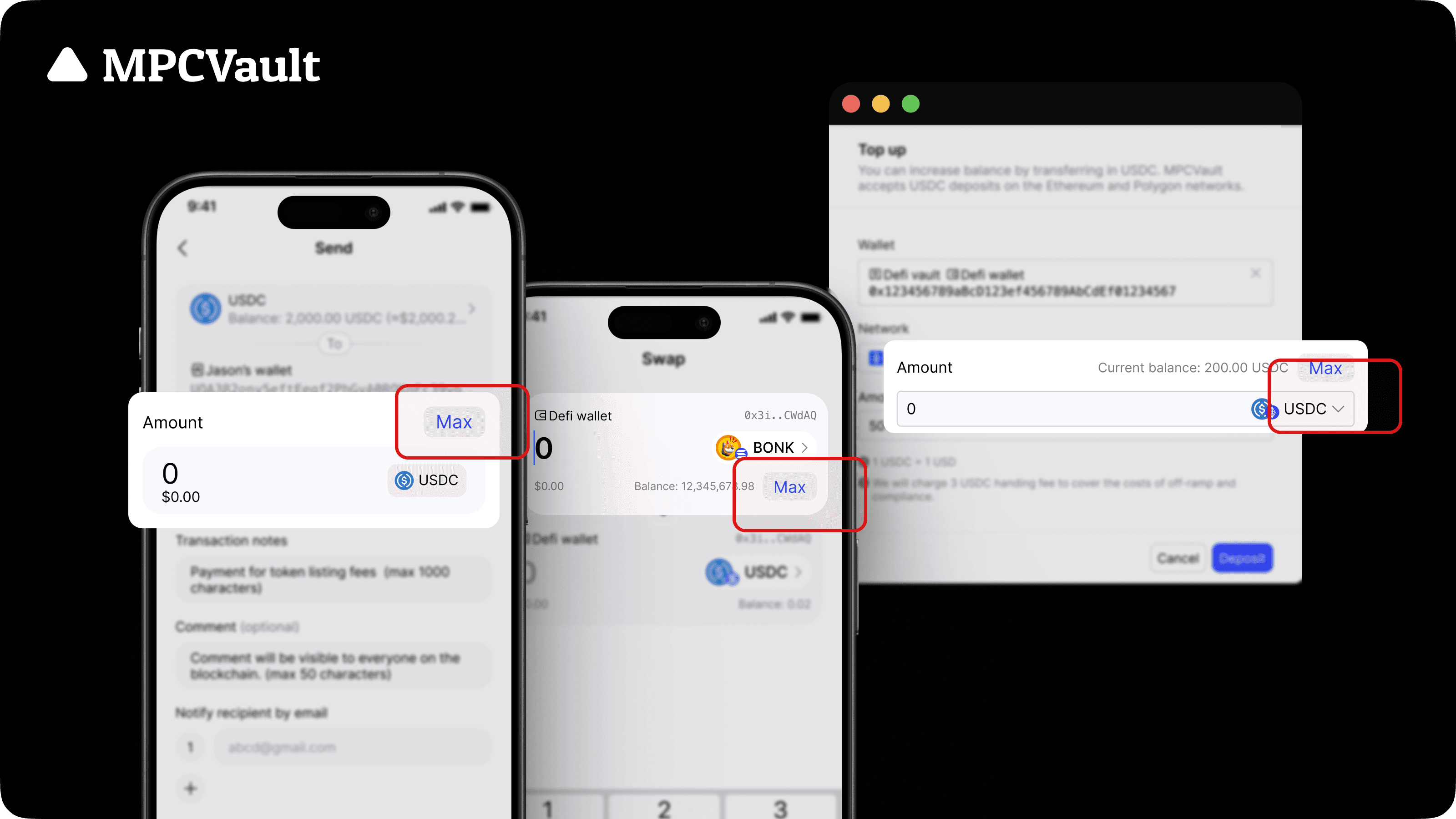
Product update, Max, App, Web Console
Introducing the "Max" button for non-native tokens

Julie
•
Sep 9, 2025
Read More
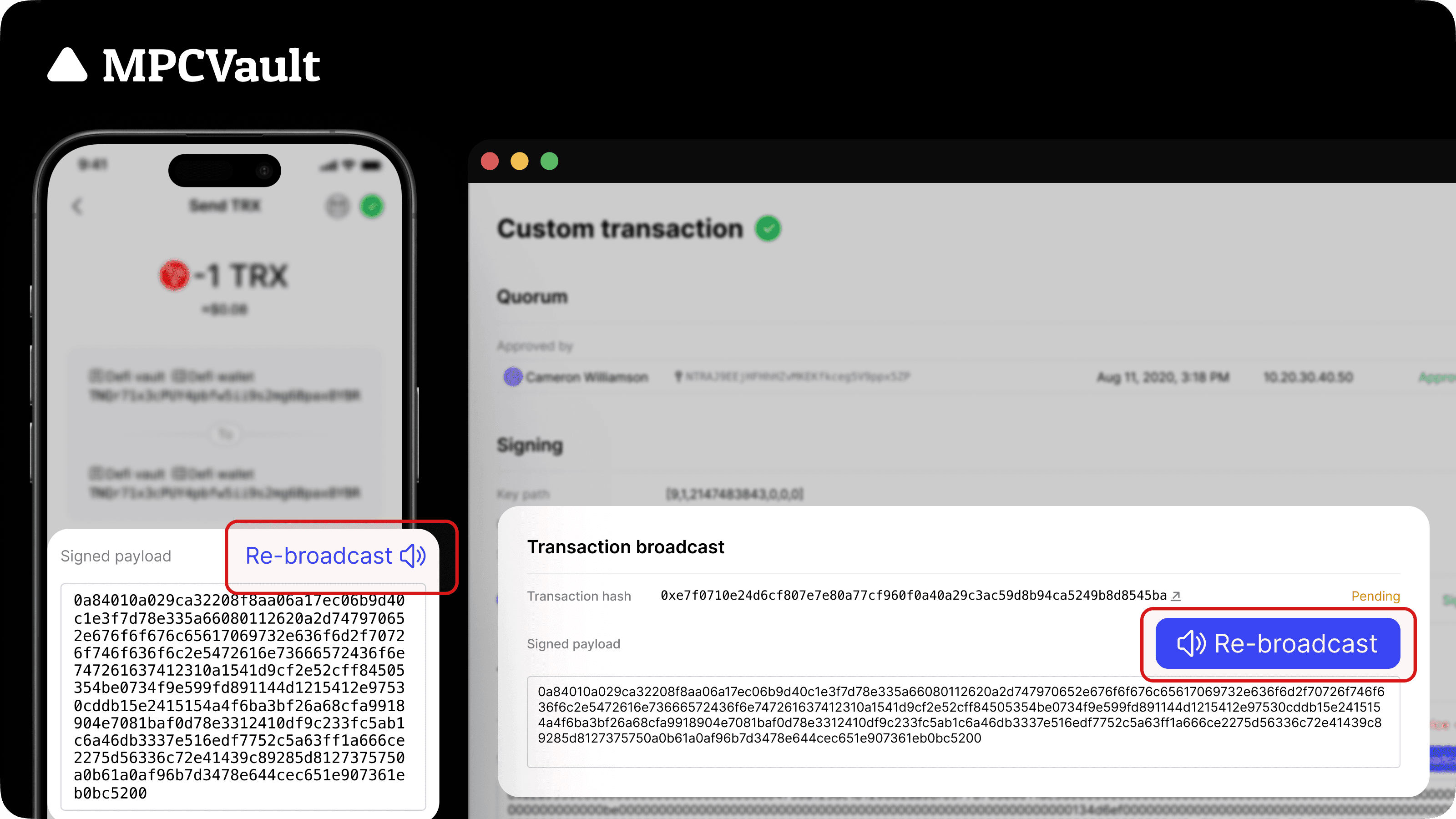
Product update, Re-broadcast, App, Web Console
New "Re-broadcast" button for non-EVM transactions

Julie
•
Sep 3, 2025
Read More

Product update, dApp, DeFi, App
dApp connections now available on mobile app

Julie
•
Jul 11, 2025
Read More

Product update, UI, App
Upgraded app home page “+” menu

Julie
•
Jul 9, 2025
Read More
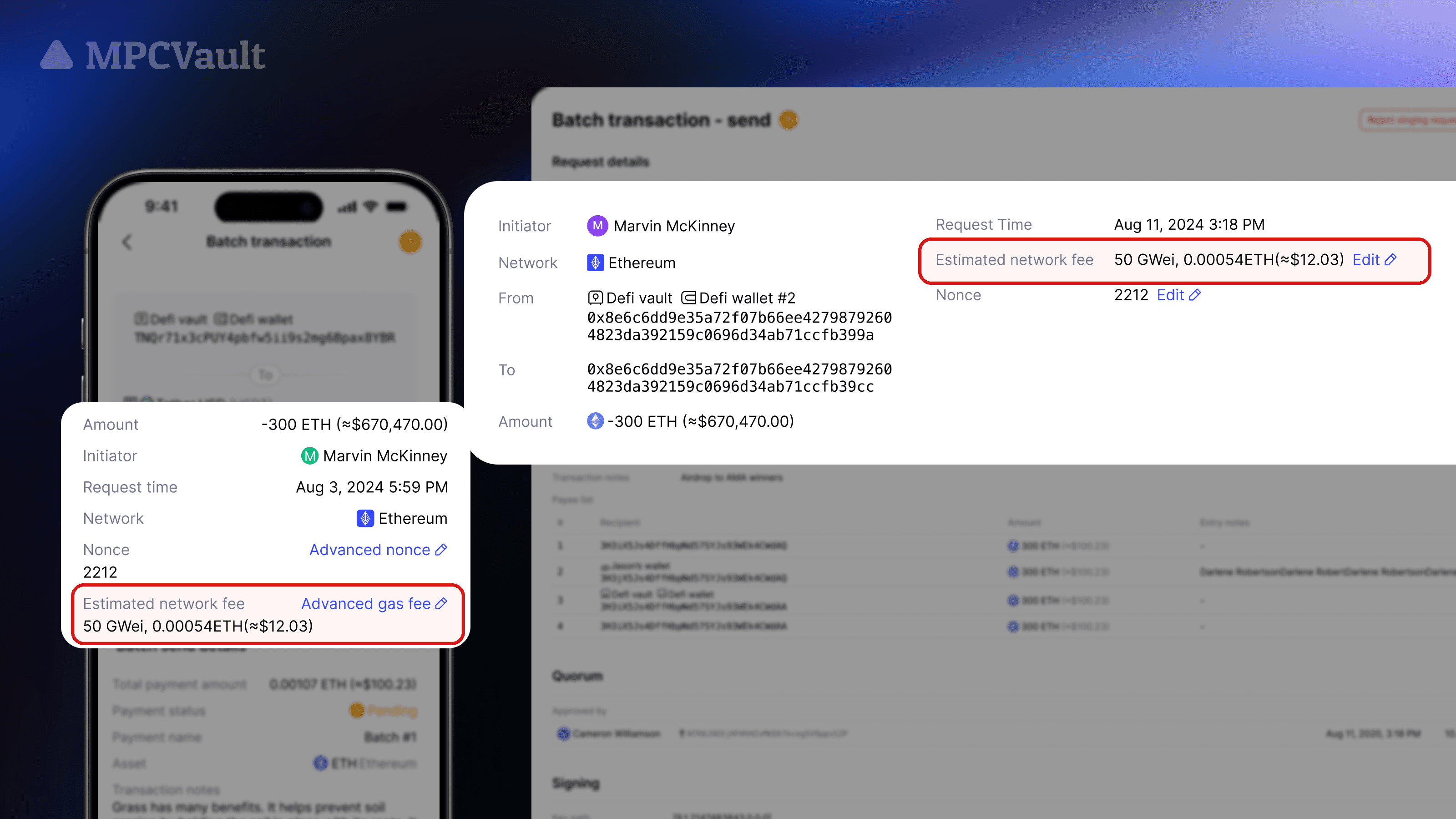
Product update, Batch Payment
Batch Transaction now Supports Gas Fee Configurations

Julie
•
Jun 27, 2025
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, Story
MPCVault Now Supports Story: Unlocking New Possibilities for On-Chain IP Assets

Julie
•
Jun 11, 2025
Read More

Product update, Off-ramp
Off-Ramping Now Live – Convert Stablecoins to Fiat Instantly

Julie
•
May 12, 2025
Read More
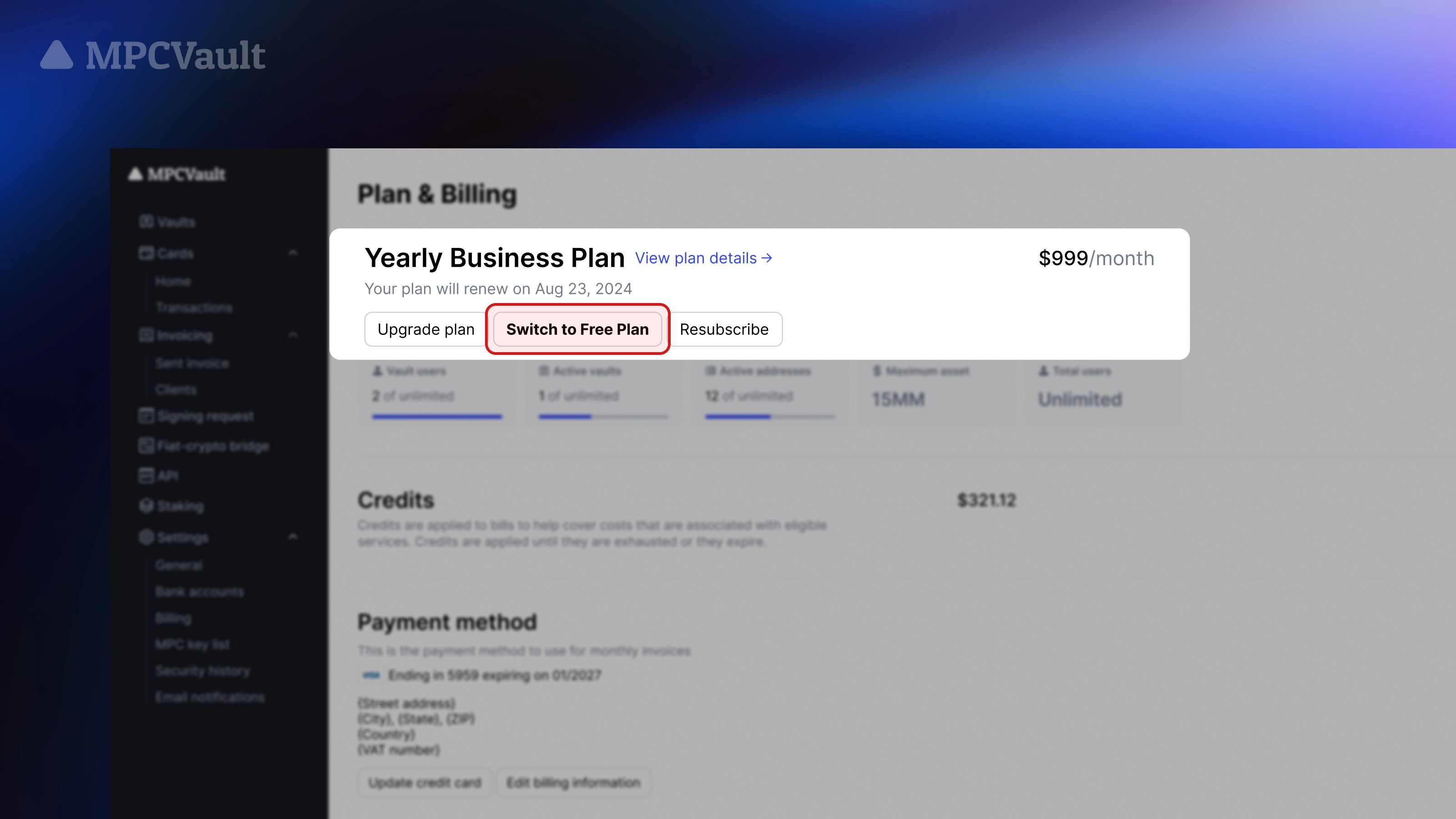
Product update, Plans, Self-serve
Self-Serve Downgrade to Free Plan

Julie
•
May 9, 2025
Read More

Tron
Tron Wallet

Eddy
•
May 6, 2025
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, Story
Now Live: MPCVault Integrates with Story

Julie
•
May 5, 2025
Read More
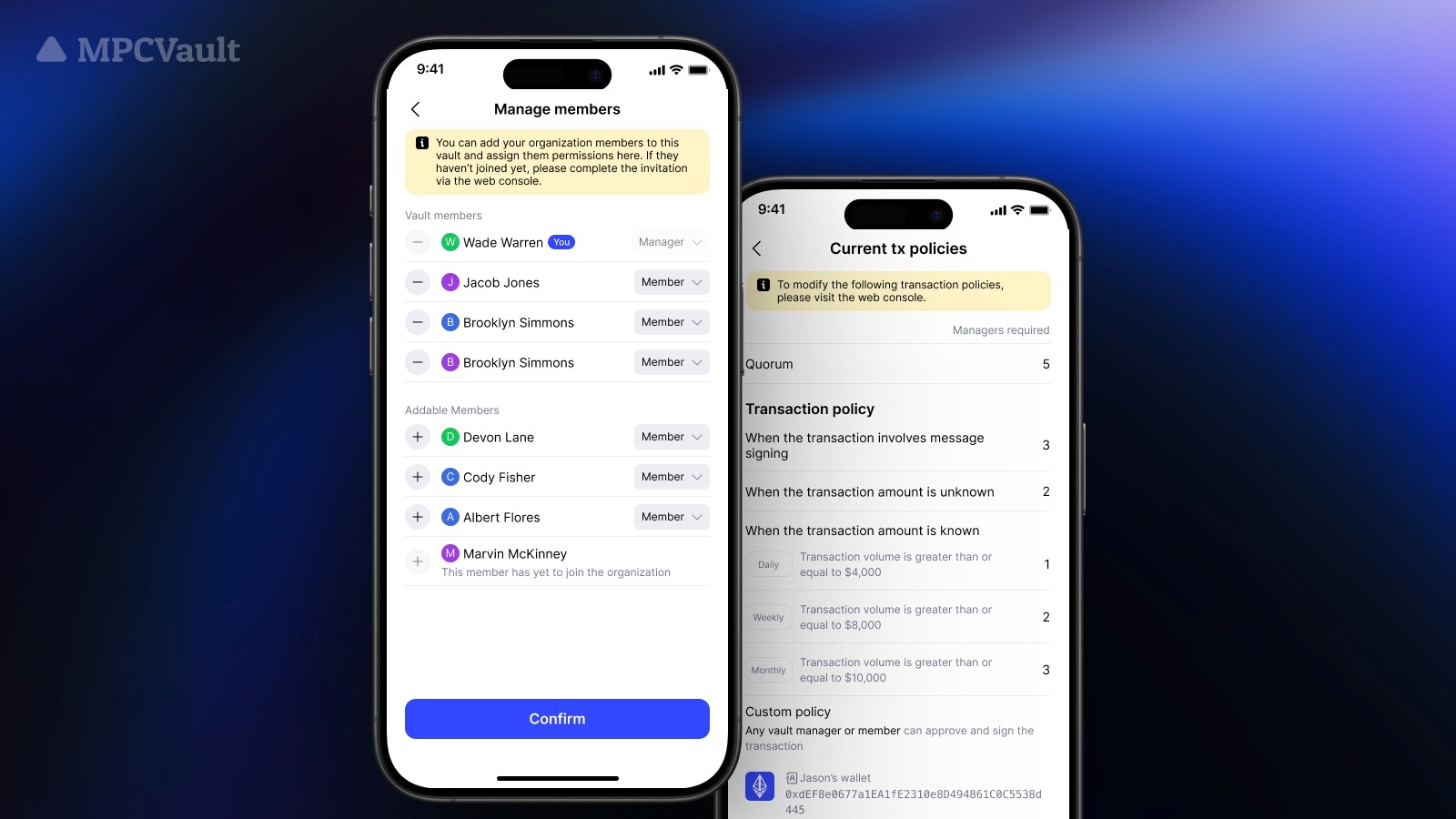
Product update, Transaction Policy, App
New on App — Vault Member Management & Transaction Policy View

Julie
•
May 1, 2025
Read More
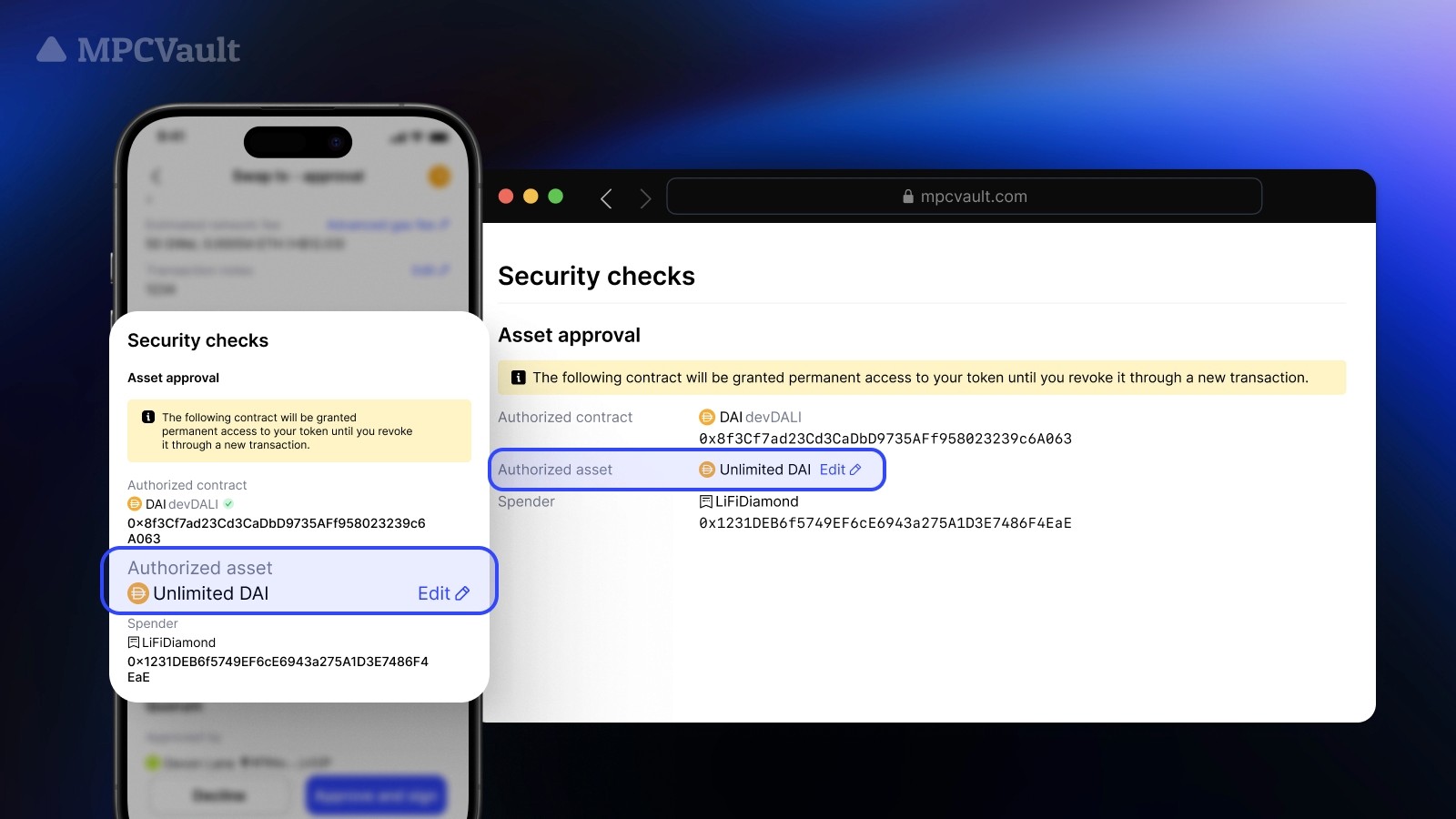
Product update, Assets, App, Web Console
Adjustable Asset Approval Amounts

Julie
•
Apr 29, 2025
Read More
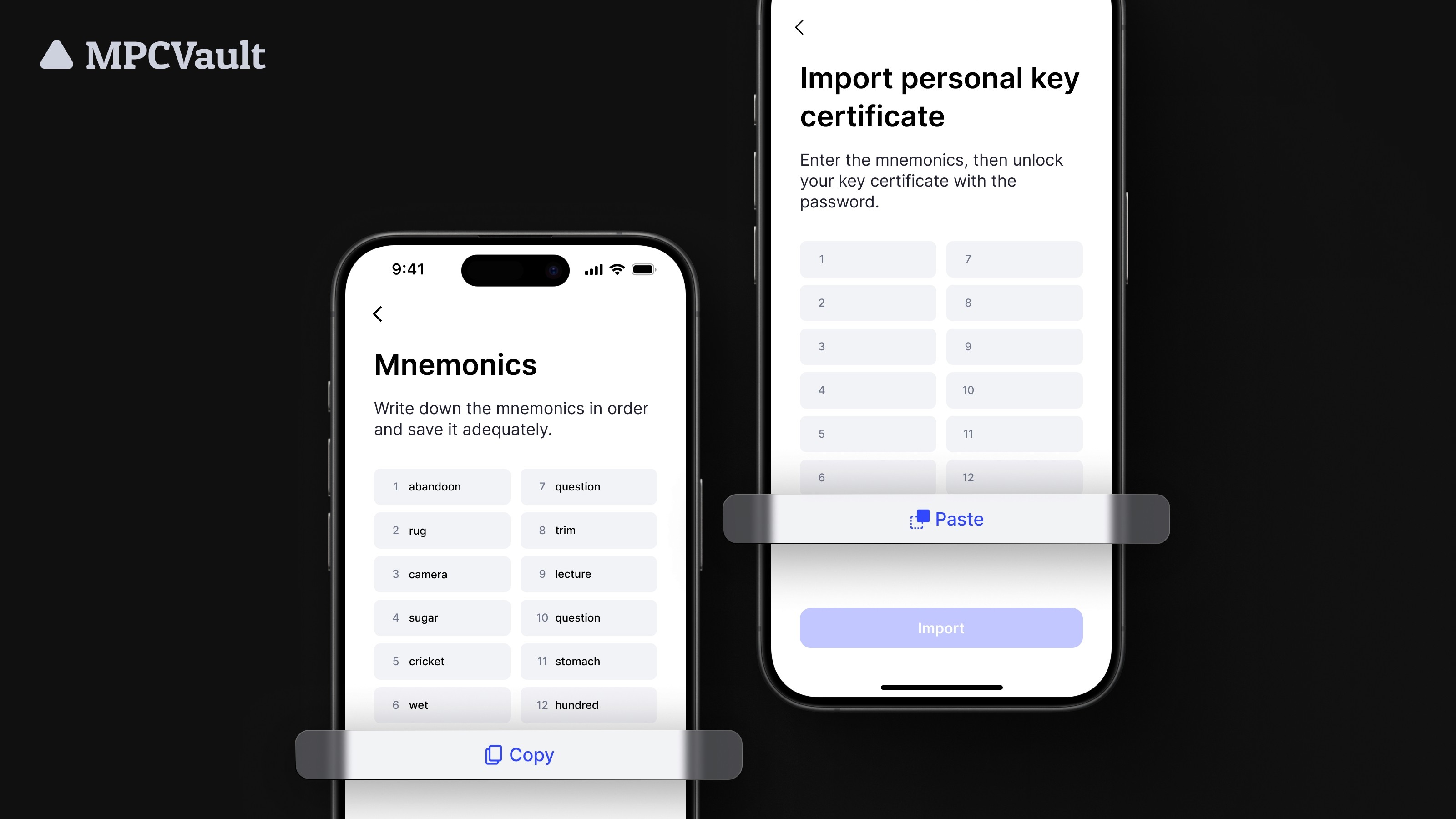
Product update, App
Faster Key Certificate Backup with Mnemonics

Julie
•
Apr 25, 2025
Read More

Product update, Card, App, Web Console
Top up MPCVault Card with Solana USDC

Julie
•
Apr 23, 2025
Read More

Product update, API, Developers
REST API Interface Now Available

Julie
•
Apr 19, 2025
Read More

Product update, Sonic SVM, Blockchain Integration
New Blockchain Integration: Sonic SVM

Julie
•
Apr 17, 2025
Read More
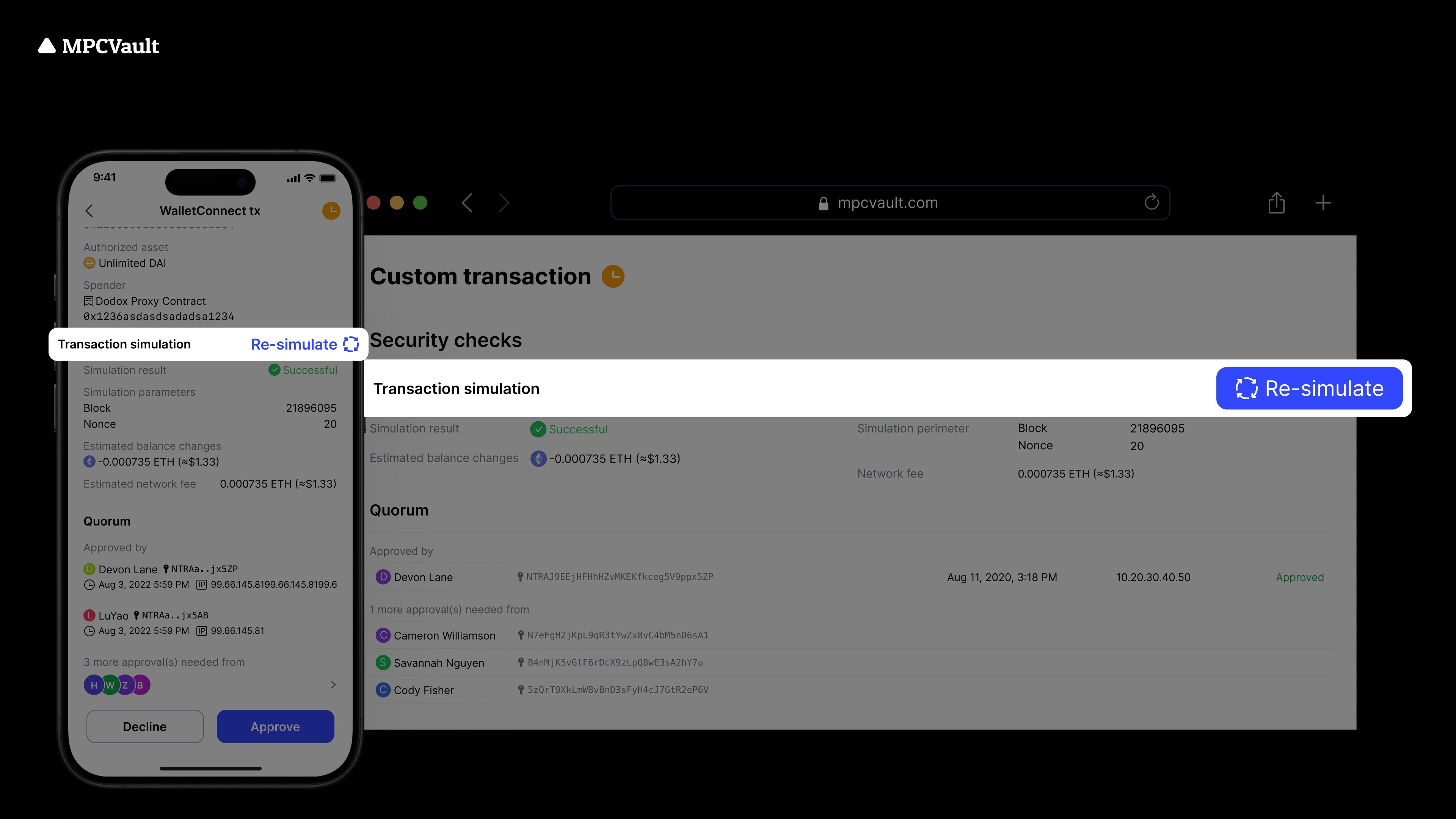
Product update, Re-simulate, App, Web Console, Developers
Re-simulate Transactions before Signing

Julie
•
Apr 10, 2025
Read More

Product update, App
View Token Details and Manage Spam Tokens on Mobile App

Julie
•
Apr 6, 2025
Read More

BTC
BTC Wallet

Eddy
•
Apr 2, 2025
Read More
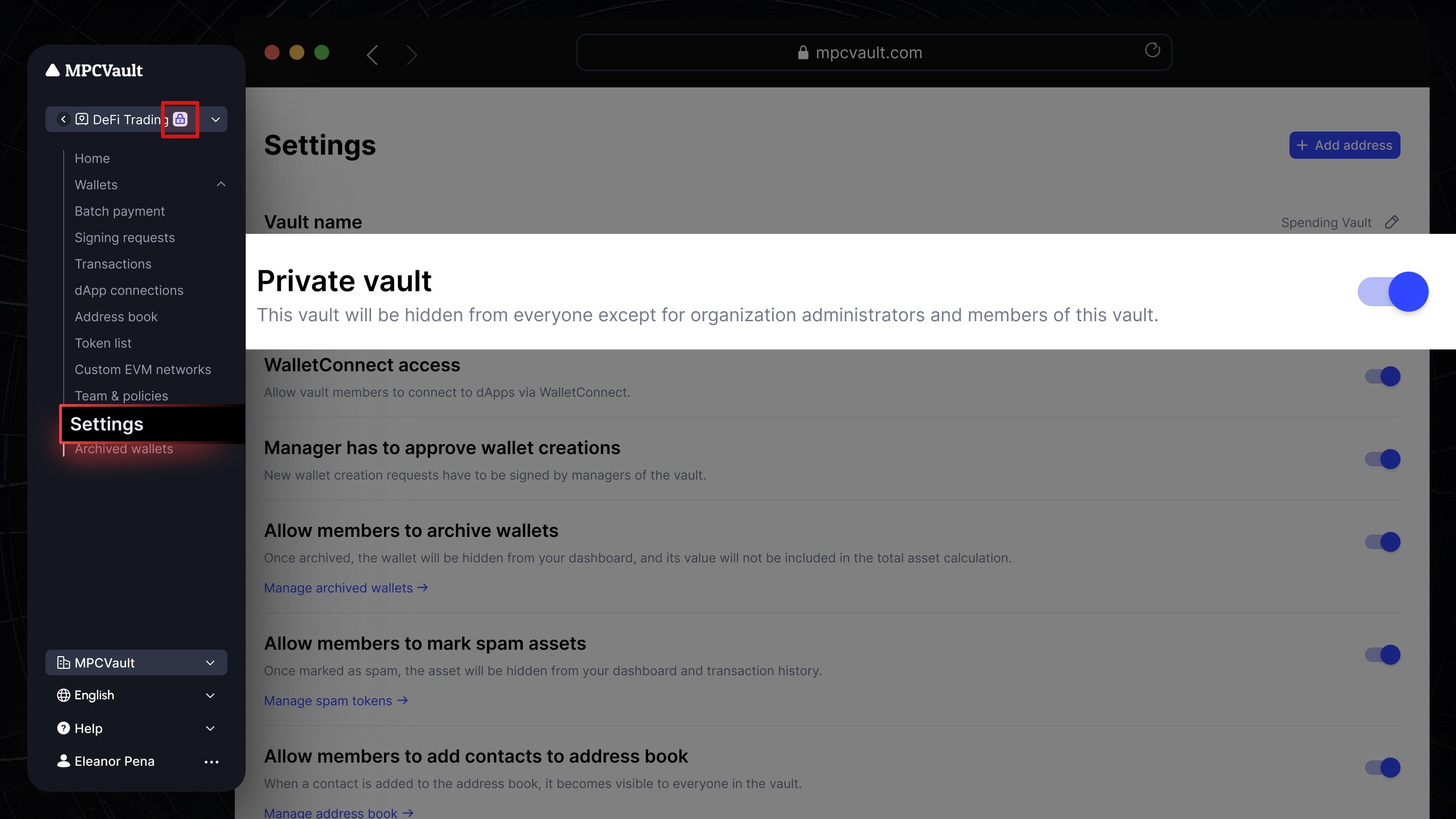
Product update, Vault
Private Vaults — Enhanced Access Control

Julie
•
Mar 28, 2025
Read More

Product update, App
Automatic Transaction Refresh on Mobile App

Julie
•
Mar 15, 2025
Read More
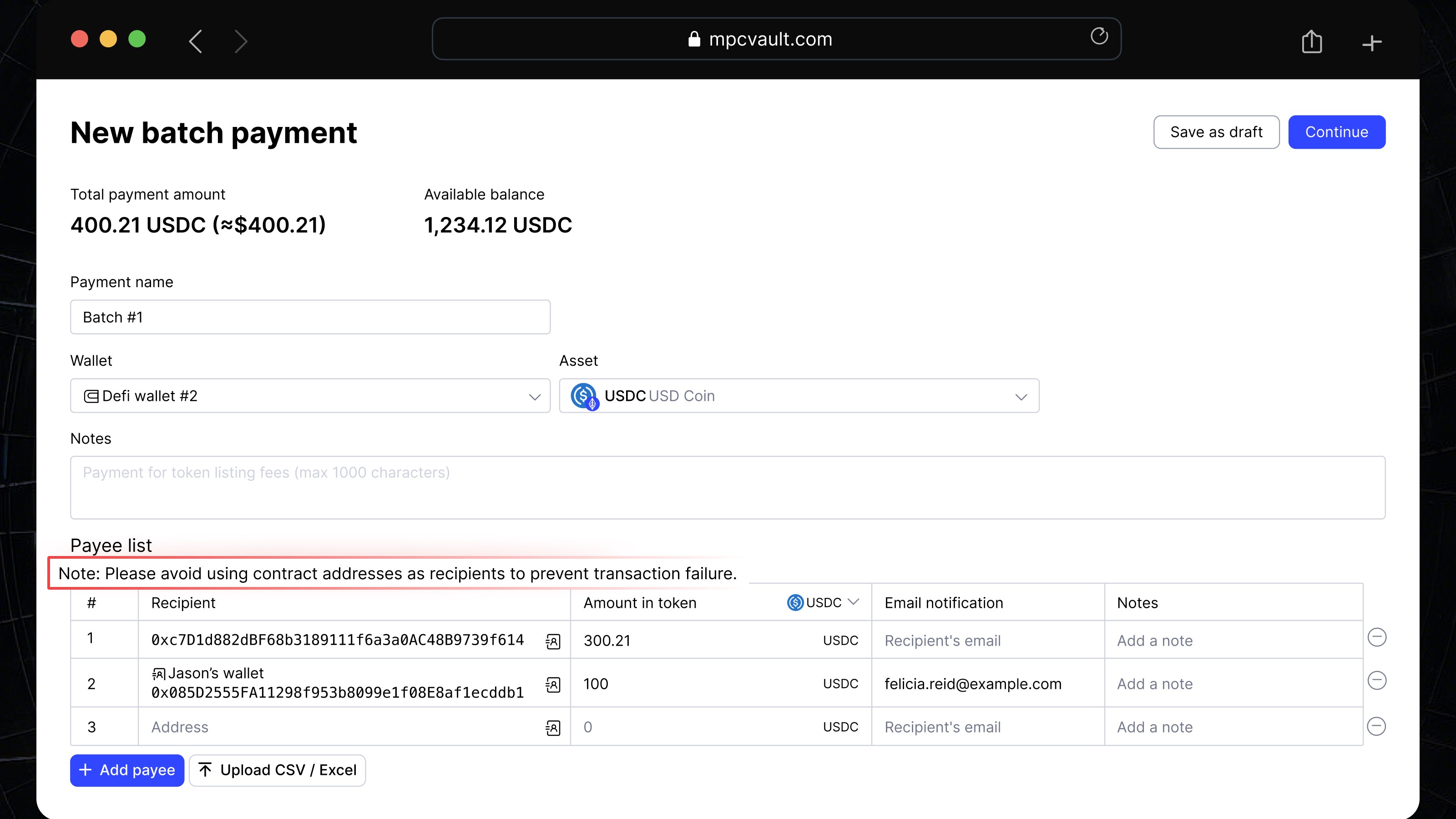
Product update, Batch Payment, EVM
Reminder: A Note on Batch Payments

Julie
•
Mar 8, 2025
Read More
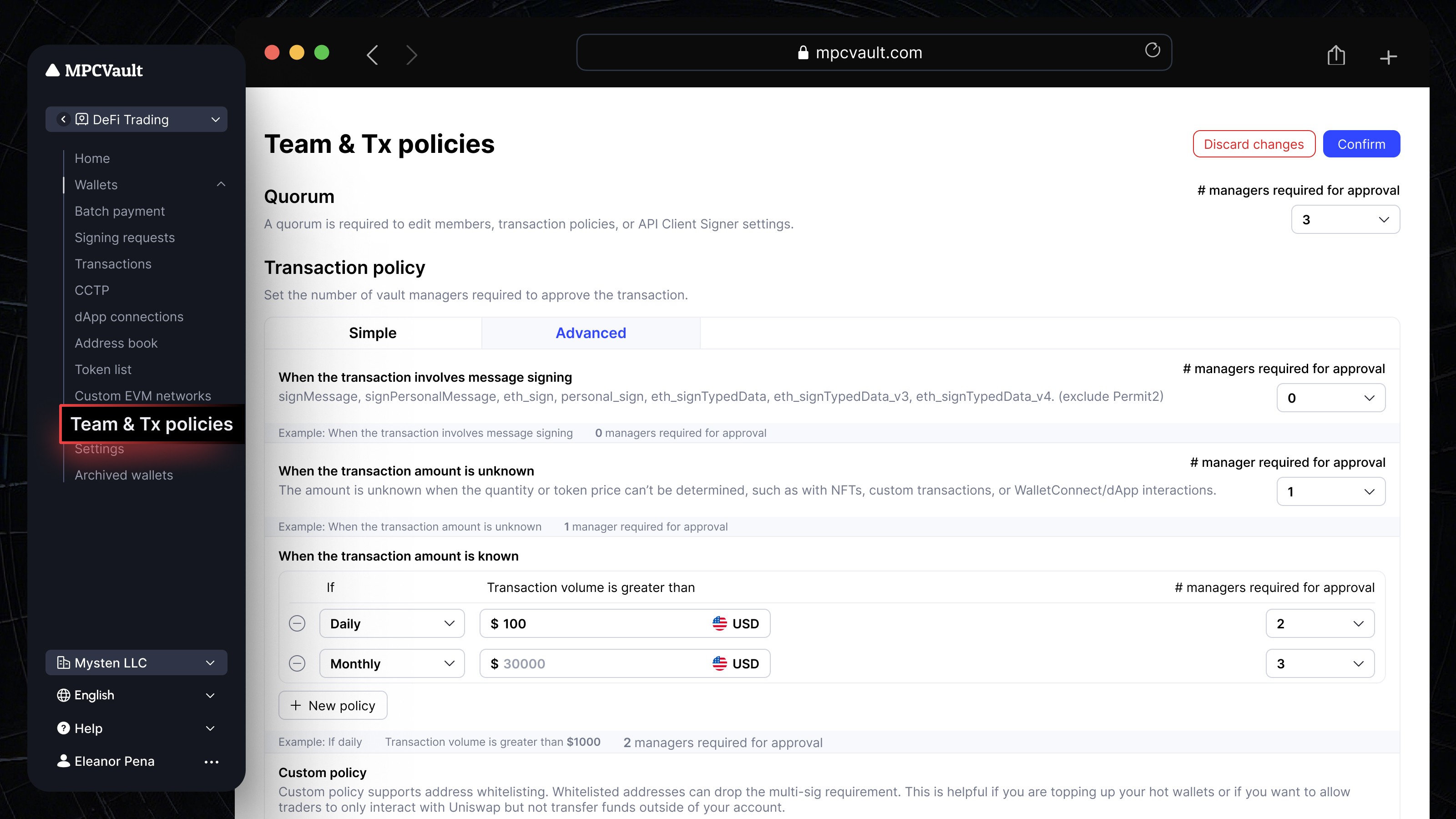
Product update, Transaction Policy
Introducing Two Transaction Policy Modes for More Flexibility

Julie
•
Mar 4, 2025
Read More
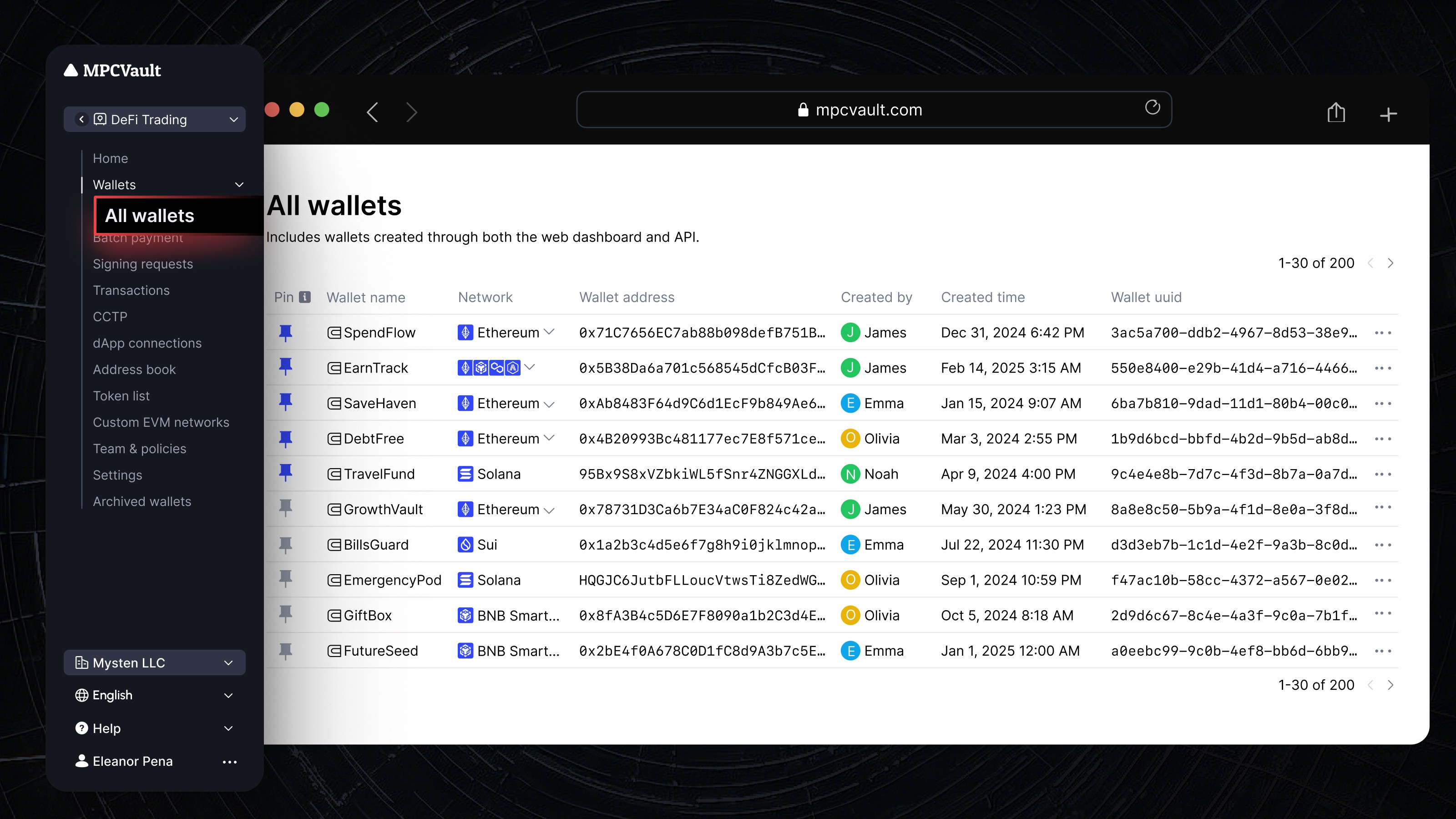
Product update, API, Wallet, Developers
A Redesigned Wallets page

Julie
•
Mar 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, Movement
Movement integration is here!

Julie
•
Feb 27, 2025
Read More
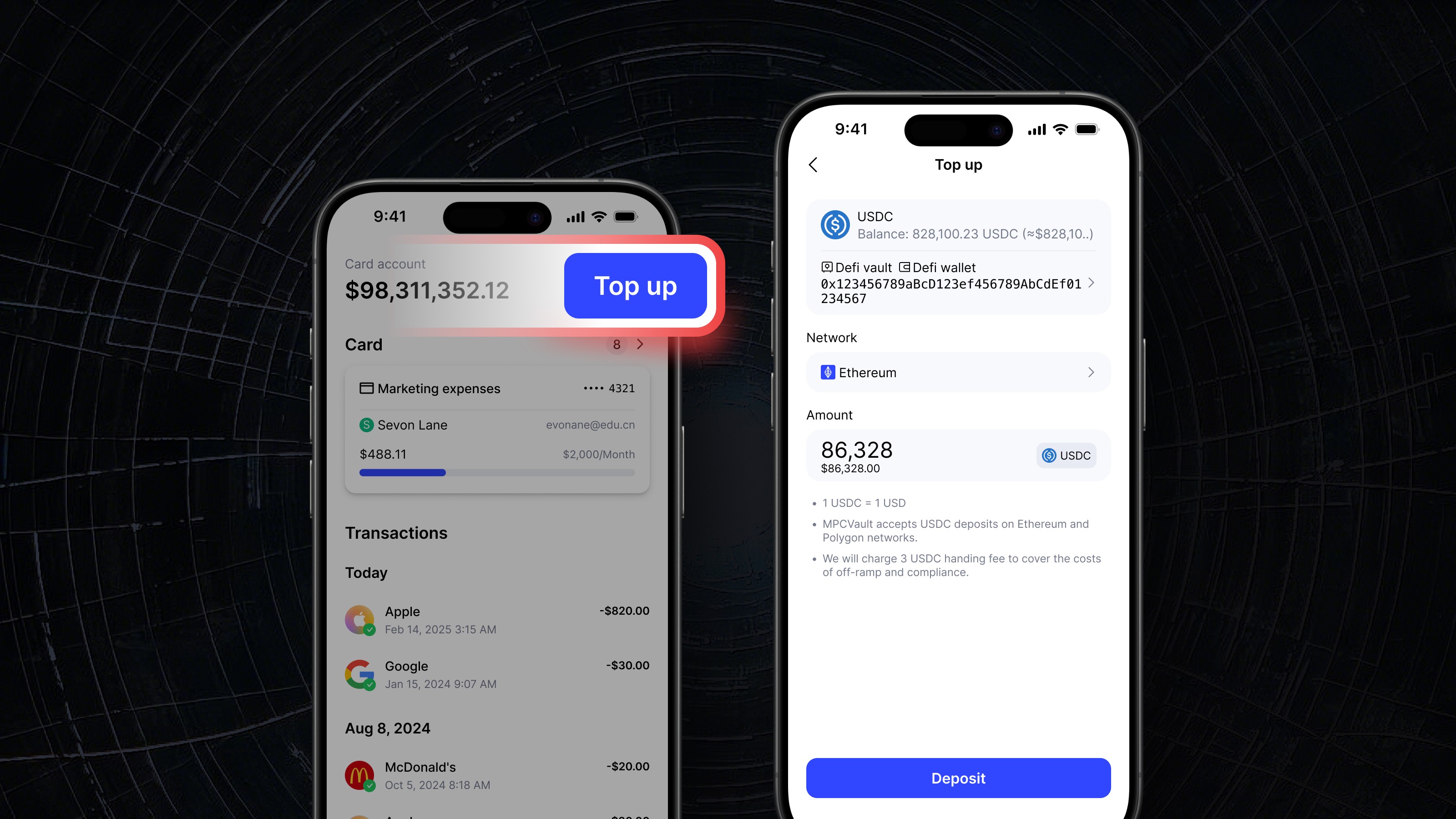
Product update, Card, App
Top Up MPCVault Card in Mobile App

Julie
•
Feb 25, 2025
Read More

Product update, Security, Solana
Accelerate Transaction & Anti-Sandwich Protection on Solana

Julie
•
Feb 21, 2025
Read More

Product update, API, Solana, Developers
Custom Transactions on Solana

Julie
•
Feb 18, 2025
Read More
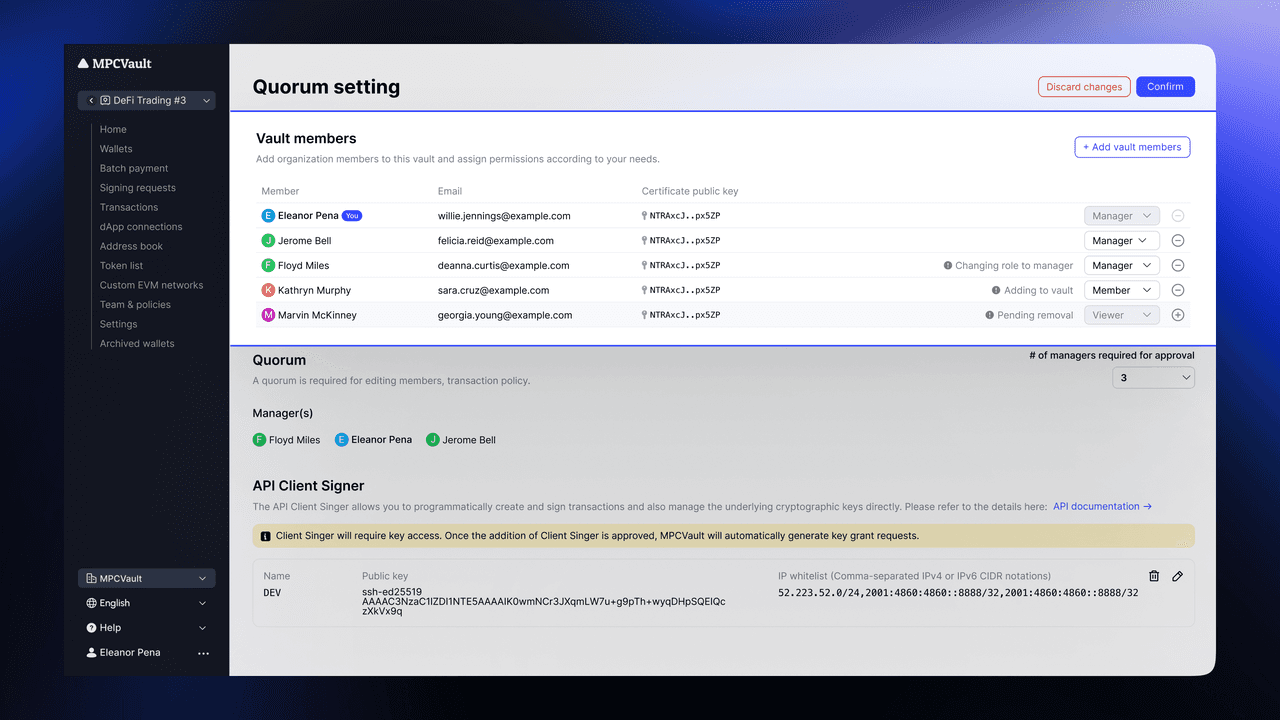
Product update, UI, Web Console
Team & Policies Page Refresh

Julie
•
Feb 11, 2025
Read More
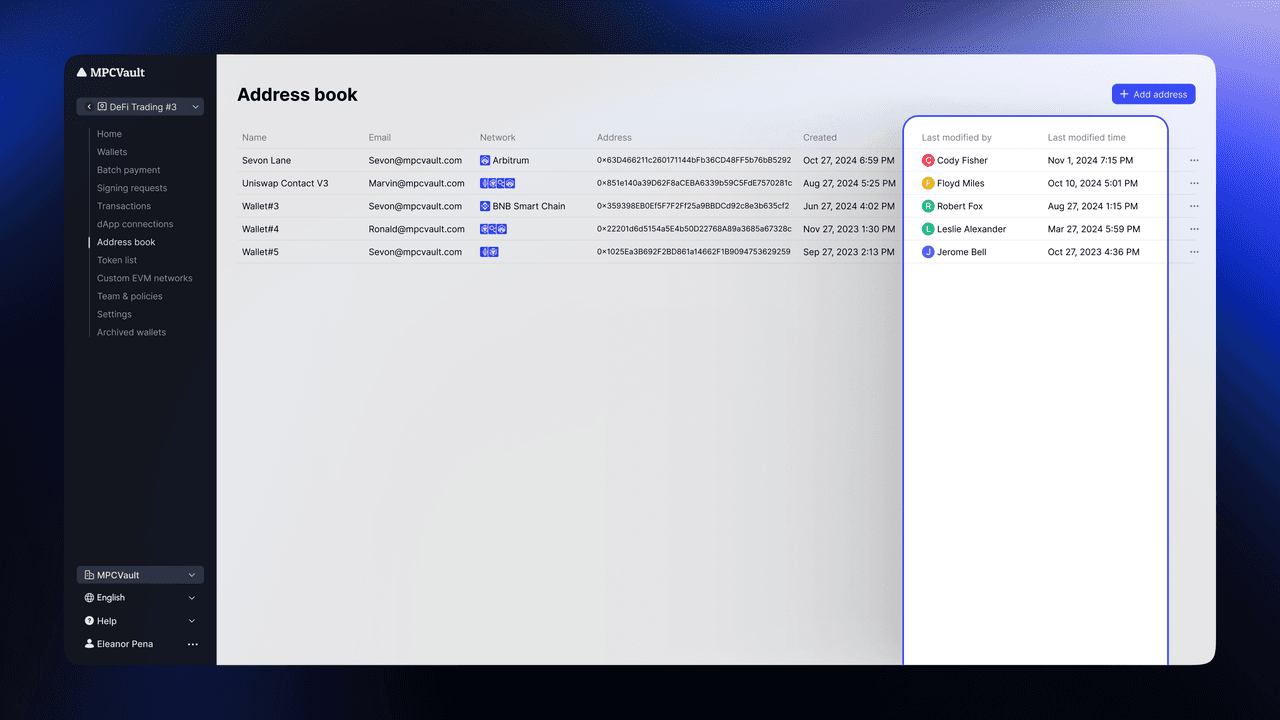
Product update, Security, Address Book, Web Console
Address Book Upgrades

Julie
•
Feb 4, 2025
Read More
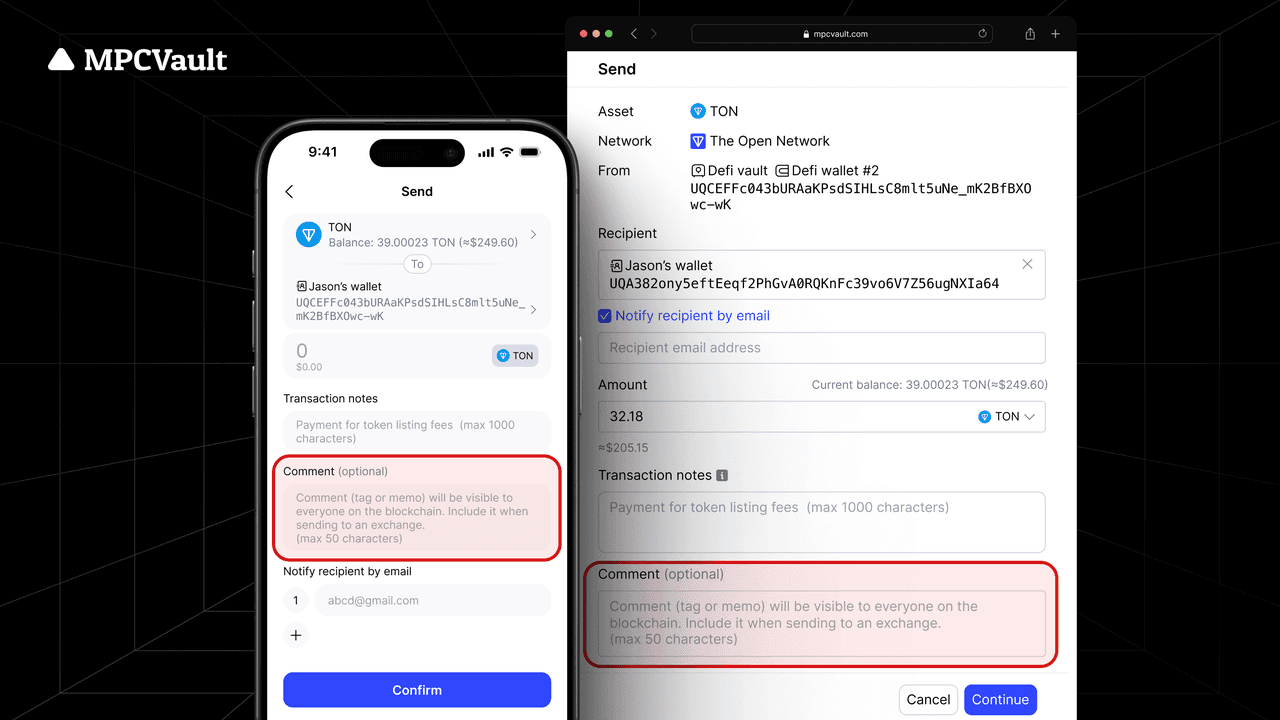
Product update, Security, TON, App, Web Console
Reminder: Proper Use of the Comment Field for TON Transactions

Julie
•
Jan 24, 2025
Read More
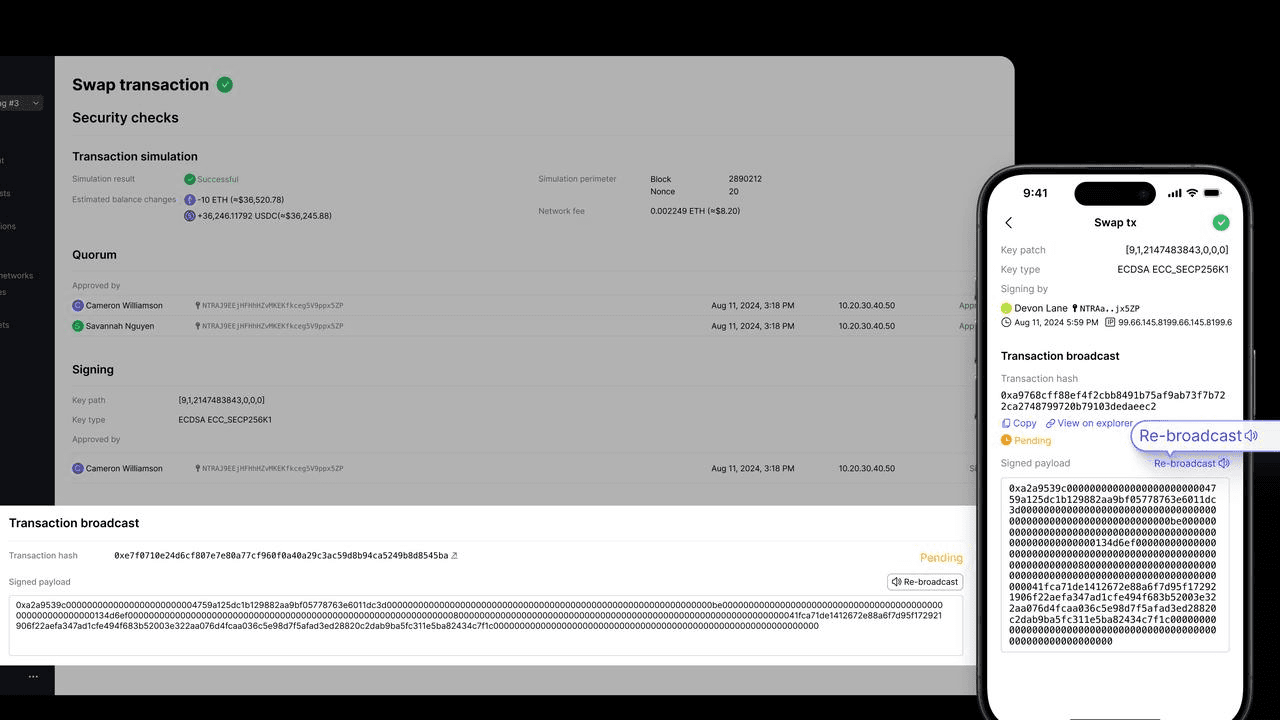
Product update, Re-broadcast, EVM, App, Web Console
New Re-broadcast Button for EVM Transactions

Julie
•
Jan 17, 2025
Read More
Product update, Solana, dApp, Developers
Improved Transaction Performance on Solana

Julie
•
Jan 10, 2025
Read More

Product update, Free Plan
Create Up to 5 Free Organizations

Julie
•
Jan 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, Paid Plan, Subscription
Subscription Renewal Grace Period

Julie
•
Dec 28, 2024
Read More

Product update, Card, Members Limits
Unlimited Organization Members

Julie
•
Dec 20, 2024
Read More

Product update, Card
MPCVault and Rain Partner to Launch the MPCVault Card: Spend USDC Anywhere Visa is Accepted

Julie
•
Dec 10, 2024
Read More

Product update, Solana, Assets, Interest-bearing tokens
Manage Interest Bearing Tokens on Solana

Julie
•
Dec 3, 2024
Read More
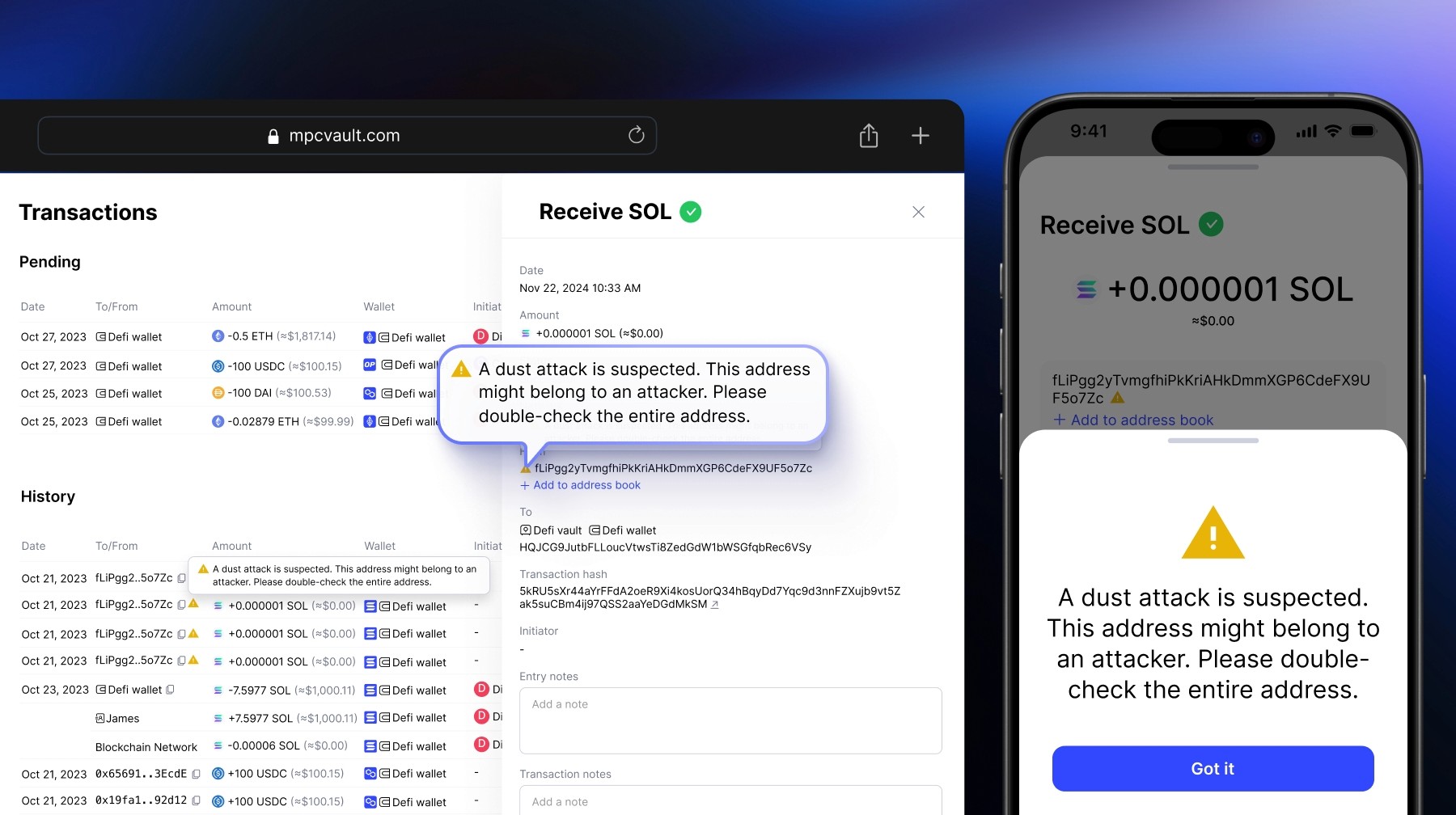
Product update, Security, Dust Transactions
Auto-detect Dust Attacks

Julie
•
Nov 30, 2024
Read More
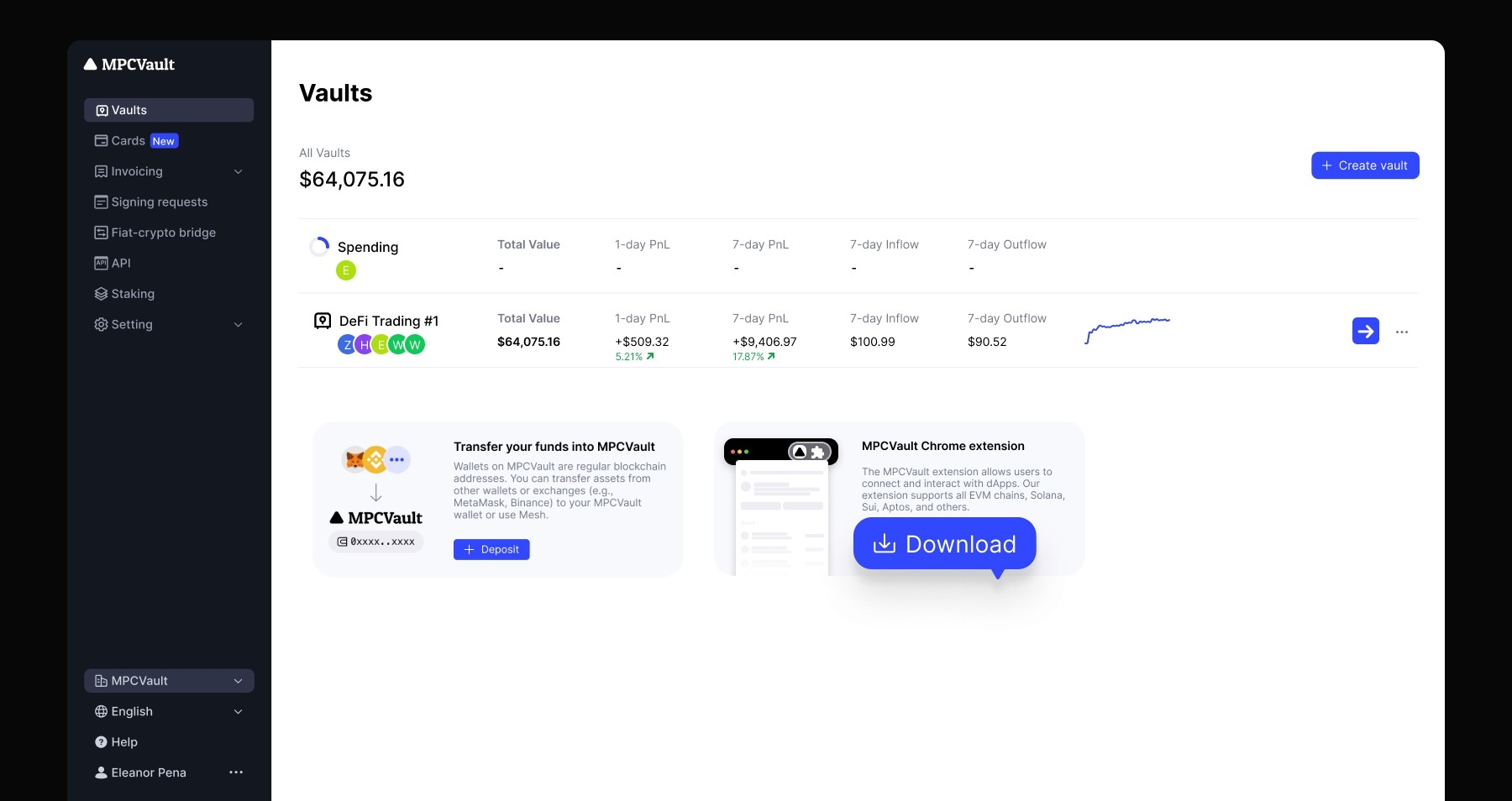
Product update, Browser Extension, dApp, Multi-chain
The MPCVault Browser Extension

Julie
•
Nov 26, 2024
Read More
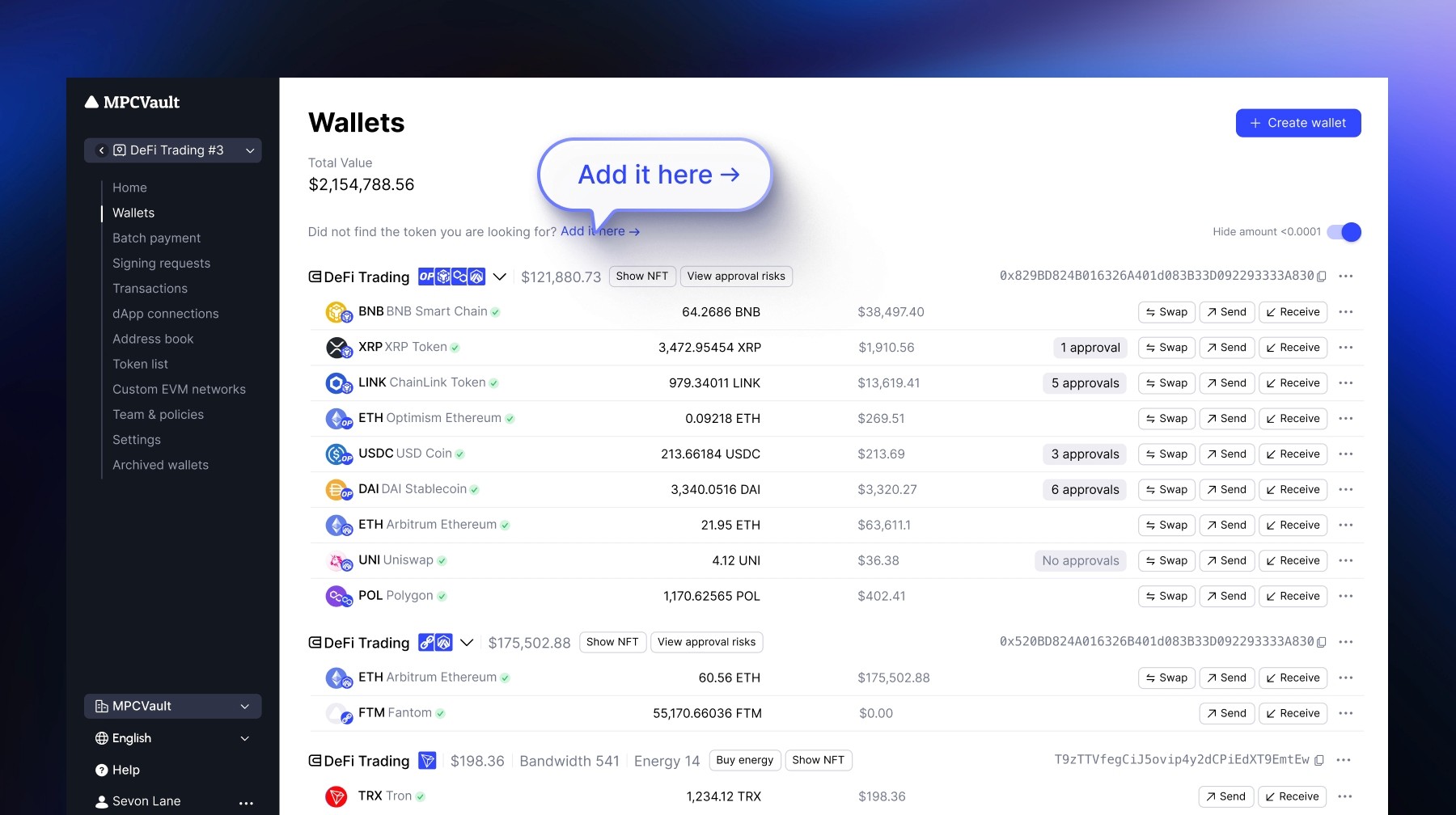
Product update, Assets, Unlisted Tokens, Web Console, Developers
New Shortcut for Importing Tokens

Julie
•
Nov 20, 2024
Read More
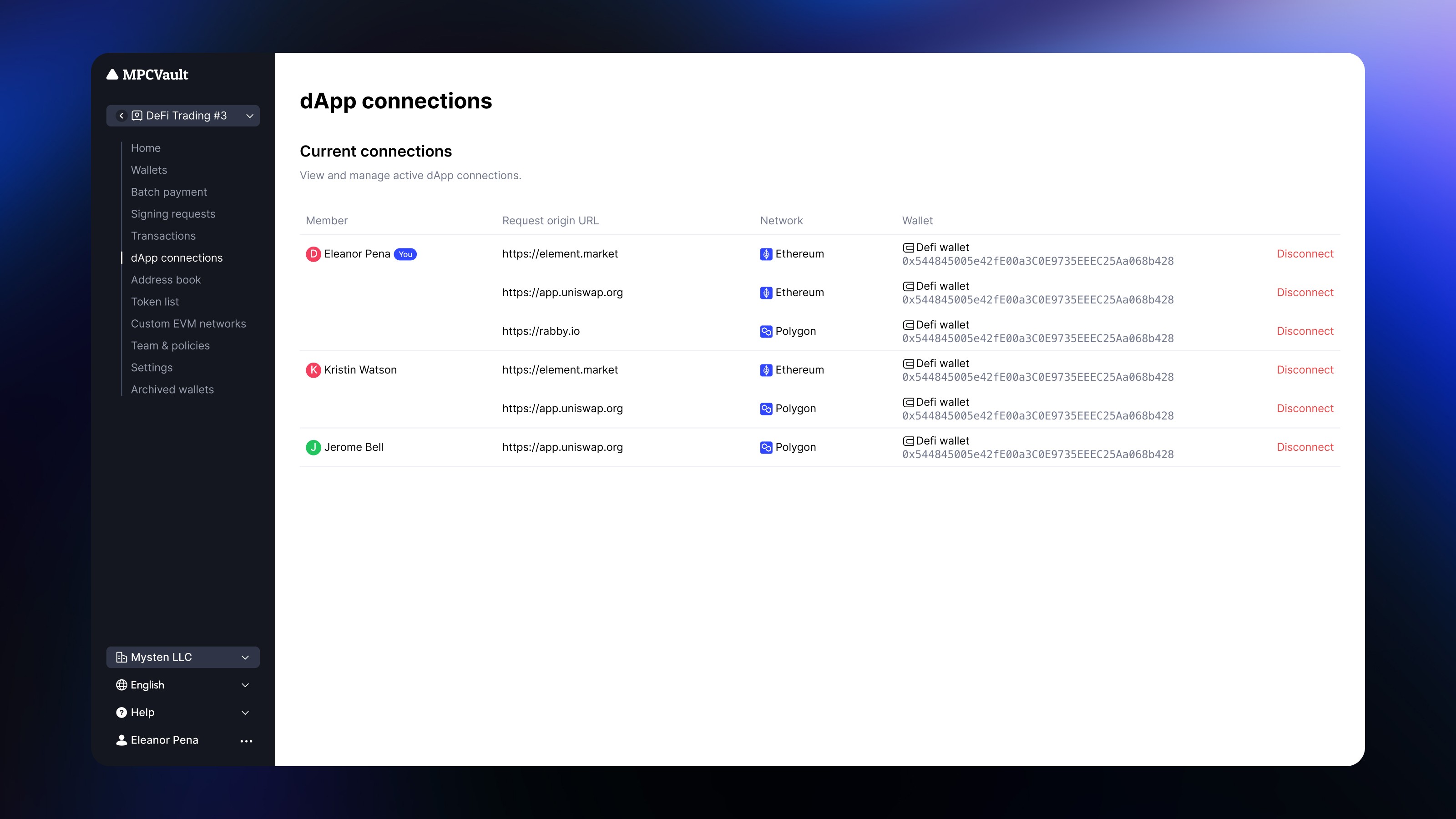
Product update, dApp, Web Console
Manage dApp Connections

Julie
•
Nov 12, 2024
Read More
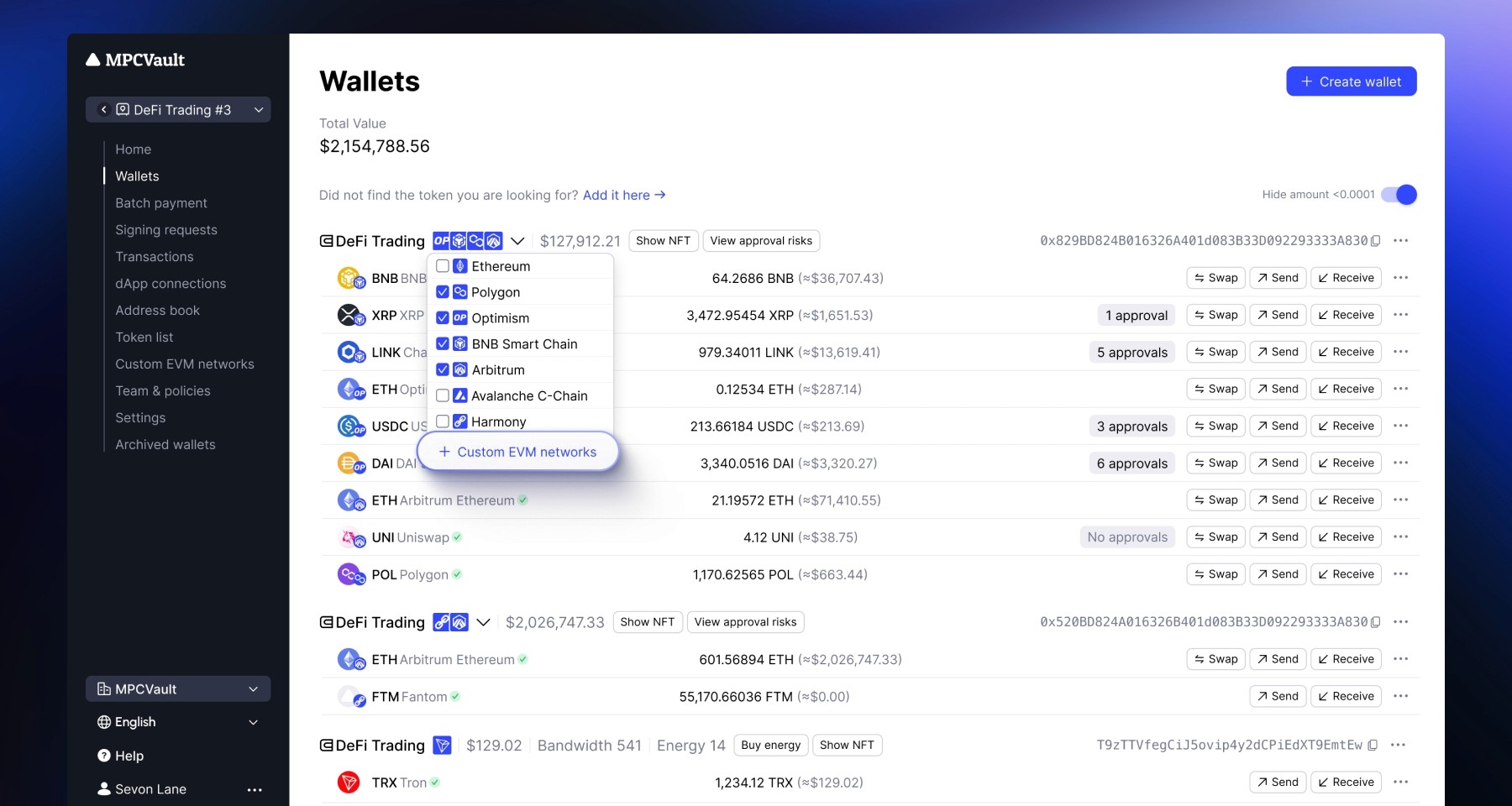
Product update, Custom EVM Chain, Web Console, Developers
Add Custom EVM Networks

Julie
•
Nov 9, 2024
Read More

Product update, Card
Launching MPCVault Card: Pay for Real World Services with Crypto

Julie
•
Nov 7, 2024
Read More
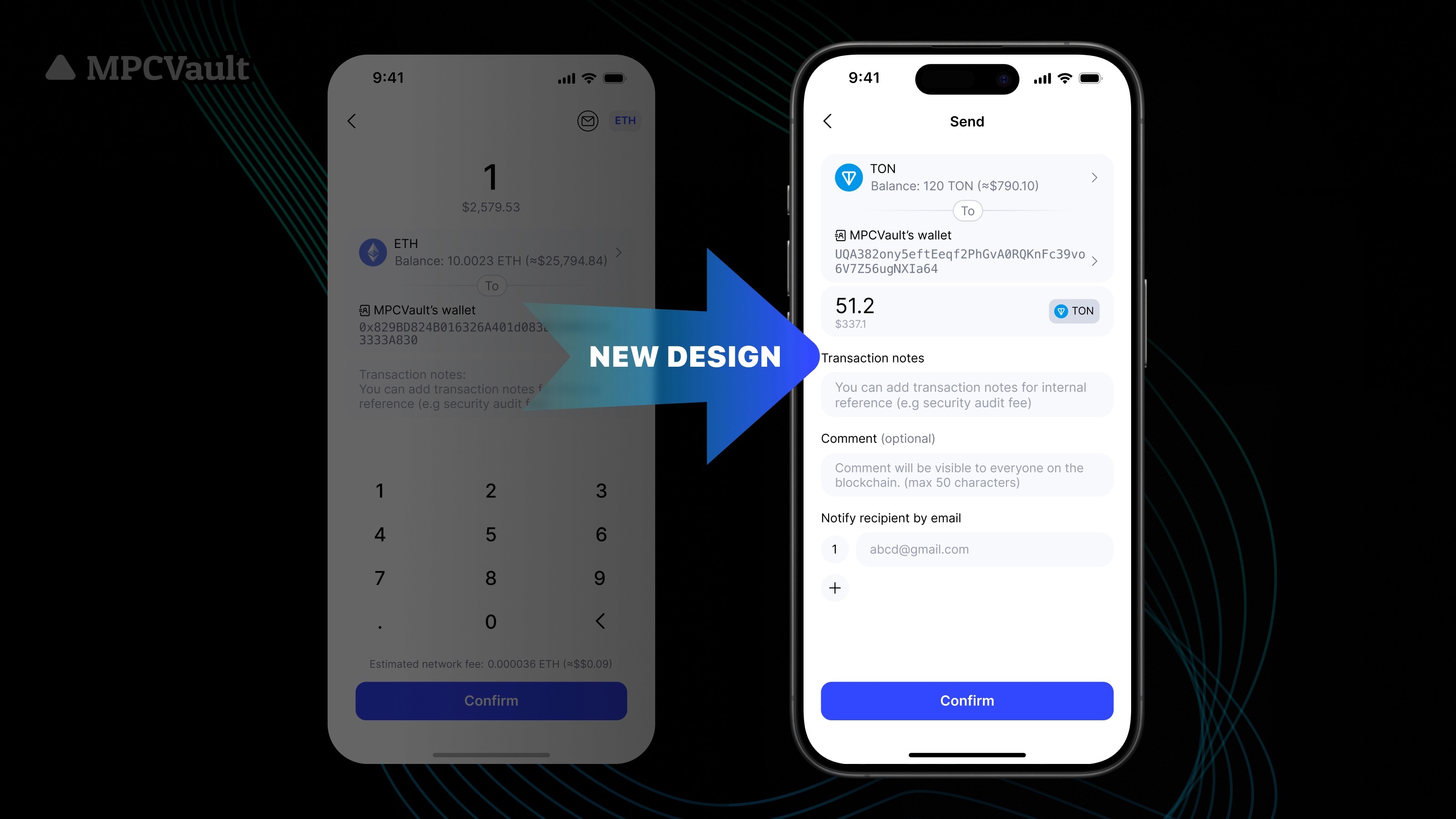
Product update, UI, App
Brand New Send Page on Mobile App

Julie
•
Nov 6, 2024
Read More

Product update, Browser Extension, RPC
Improved RPC Reliability for Browser Plugin

Julie
•
Nov 2, 2024
Read More
Alchemy
MPCVault Featured on Alchemy's List of Top MPC Wallets

Julie
•
Oct 29, 2024
Read More

Product update, Browser Extension, dApp, TON
TON Integration for Browser Plugin

Julie
•
Oct 25, 2024
Read More
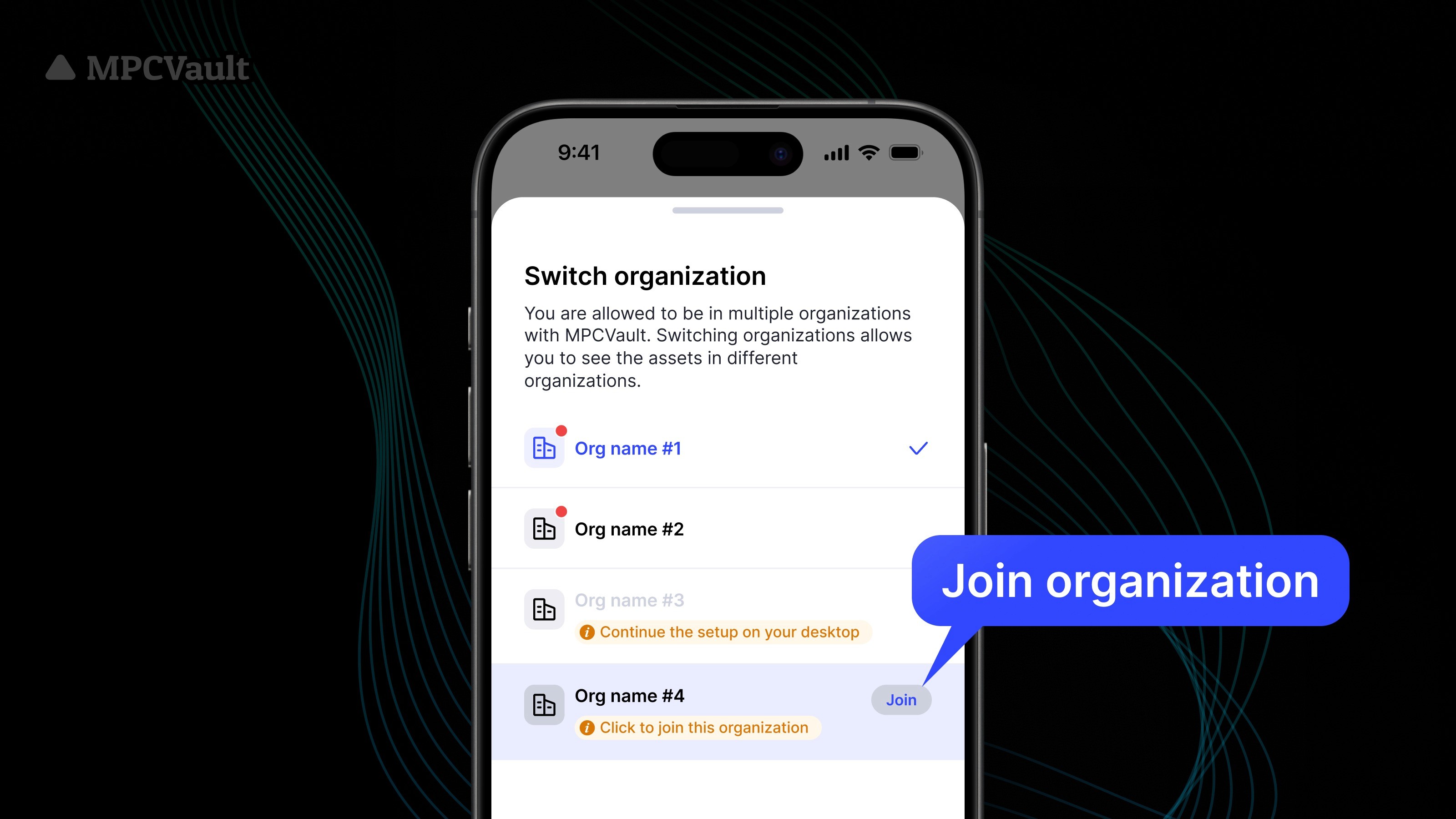
Product update, UI, App
Switching between Organizations Made Easier

Julie
•
Oct 21, 2024
Read More
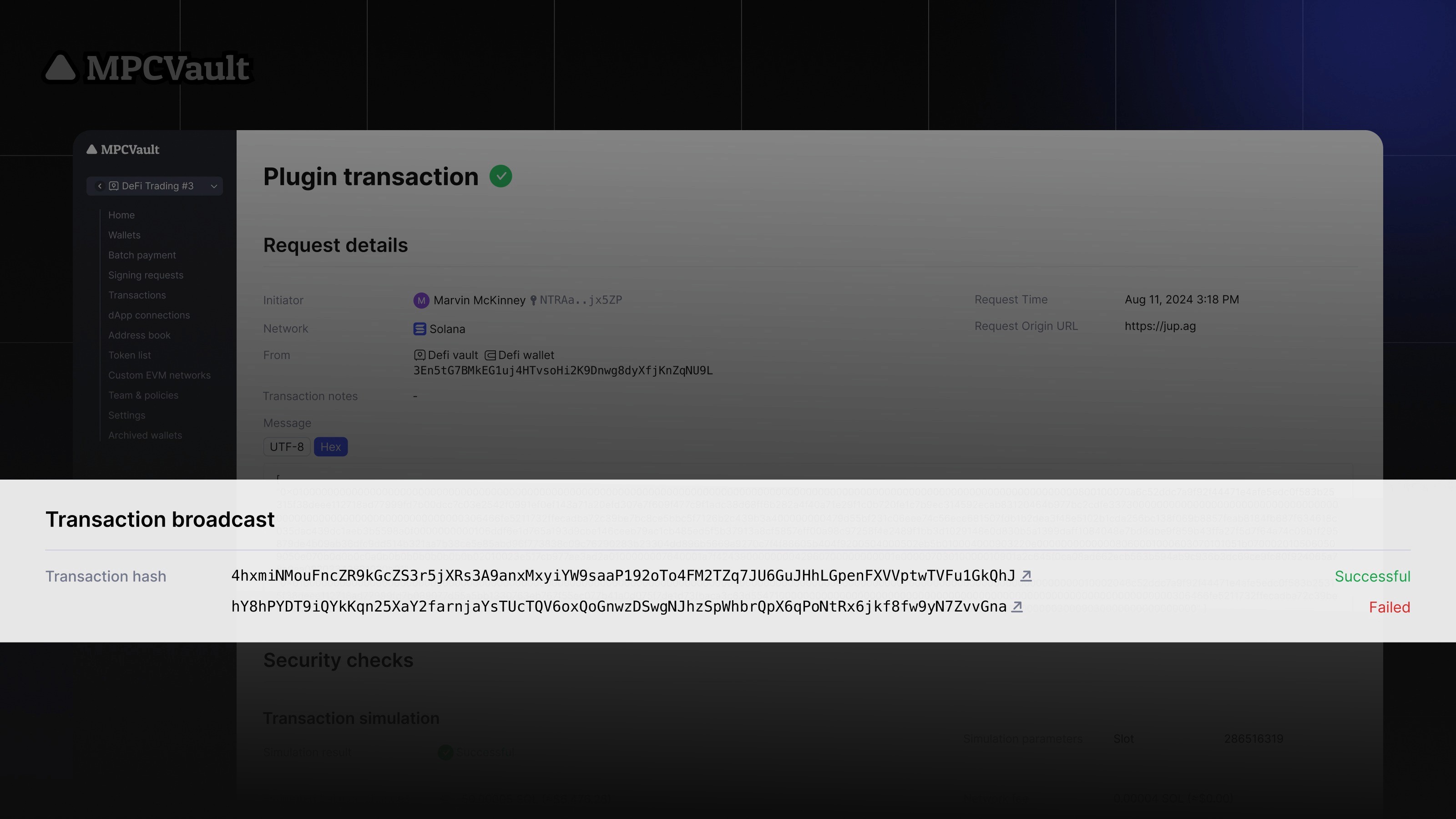
Product update, Solana, dApp, Developers
Multi-Transaction Support on Solana

Julie
•
Oct 17, 2024
Read More

Product update, Solana, Assets, Token-2022
Support for Solana's Token-2022 is now live

Julie
•
Oct 9, 2024
Read More

Alchemy
MPCVault Featured on Alchemy's List of Top MPC Wallets

Julie
•
Oct 8, 2024
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, TON
MPCVault Now Supports TON

Julie
•
Sep 16, 2024
Read More

Cryptography, MPC
Homomorphic Encryption and Secure Multiparty Computation (MPC)

Webster
•
Aug 28, 2024
Read More

Security, SOC 2
MPCVault renews SOC 2 Type II Certification for 2024

Julie
•
Jun 13, 2024
Read More

Security, Tron
Maximizing Your TRON Wallet: Tips for Secure and Efficient Use

Eddy
•
Feb 4, 2024
Read More

Cross-chain, Multi-chain
Cross-Chain vs. Multi-Chain: What's the Difference?

Eddy
•
Jan 30, 2024
Read More

L1, L2
Layer 1 vs. Layer 2: What's the Difference?

Eddy
•
Jan 29, 2024
Read More

NFT, Web3
What Are NFTs? Non-Fungible Tokens Explained

Eddy
•
Jan 28, 2024
Read More

Web3, DeFi
The Evolution of Finance: How Web3 is Shaping the Future of Banking

Eddy
•
Jan 26, 2024
Read More

Crypto Taxes
Cryptocurrency Taxation: Navigating the Complex World of Crypto Taxes

Eddy
•
Jan 16, 2024
Read More

Polygon, Security
The Trust Factor: Ensuring Transparency with Polygon Wallet Solutions

Eddy
•
Jan 12, 2024
Read More

Layer-2
What Is L2? Crypto Layer 2 Explained

Eddy
•
Jan 5, 2024
Read More

Aptos, Security
Aptos Wallet Security: How to Keep Your Digital Assets from Harm's Way

Eddy
•
Dec 28, 2023
Read More

Sui, Security
Choosing the Best Sui Wallet: Essential Tips for Crypto Users

Eddy
•
Dec 18, 2023
Read More

POS, POW, Blockchain
The Proof is in the Pudding: Understanding Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake

Eddy
•
Dec 16, 2023
Read More

Ethereum, Security
Stay One Step Ahead: Proven Methods to Prevent Ethereum Scams

Eddy
•
Dec 5, 2023
Read More

Ethereum, Security
Beware of Scammers: Common ETH Scams and How to Spot Them

Eddy
•
Nov 30, 2023
Read More

Smart Contract
What Are Smart Contracts on Blockchain and How Do They Work?

Eddy
•
Nov 22, 2023
Read More

Security, Best Practices, MPCVault
Securing Your Crypto Investments: Best Practices and Common Scam Techniques

Eddy
•
Nov 18, 2023
Read More

DAO, Governance, Transparency
What is a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO)? Understanding the New Era of Governance

Eddy
•
Nov 6, 2023
Read More

Stablecoins, DeFi, Payments
What Is A Stablecoin? The Safe Haven of Cryptocurrency and Its Investment Appeal

Eddy
•
Nov 3, 2023
Read More

Cross-chain, Blockchain Bridges
What is Cross-Chain?

Eddy
•
Oct 18, 2023
Read More

Multi-chain, Interoperability, Cross-chain
What is Multi-Chain?

Eddy
•
Oct 14, 2023
Read More

ICOs, STOs
ICOs vs. STOs: The Investment Opportunities and Risk Considerations

Eddy
•
Oct 5, 2023
Read More

Cryptography, MPC
Secure Multiparty Computation

Webster
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

TEE
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 1)

Eddy
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

TEE
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 3)

Eddy
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

TEE
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 2)

Eddy
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

Security
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 3)

Eddy Sang
•
Apr 7, 2023
Read More
All (91)
Product update (60)
Assets (5)
Card (6)
Security (13)
App (25)
Developers (8)
Blogs (91)

Product update, Organization accountant
Who introduced an accountant role to the organization

Julie
•
Nov 3, 2025
Read More

Product update, Transaction Policy, Whitelist Only Mode
Whitelist Transfers: restrict transactions to approved accounts

Julie
•
Nov 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, UI, App
The Liquid Glass effect is LIVE on iOS

Julie
•
Oct 27, 2025
Read More

Product update, Sui, Swap
New Sui swap and cross-chain swap options

Julie
•
Oct 20, 2025
Read More

Product update, Card
Download card transaction history via CSV

Julie
•
Oct 13, 2025
Read More

Product update, Email Notifications, Transaction Notes
Smarter email notifications: address book labels and transaction notes

Julie
•
Oct 9, 2025
Read More

Product update, Email Notifications, UX
Direct link to transaction details from email

Julie
•
Oct 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, Off-ramp, USD
Expanded transfer type for US users

Julie
•
Sep 23, 2025
Read More

Product update, Transaction Filter, App, Web Console
The new transaction filter

Julie
•
Sep 19, 2025
Read More

Product update, Assets, Mark As Spam, App
New menu in mobile app transaction details page

Julie
•
Sep 16, 2025
Read More

Product update, API, App, Web Console
Show API requests in the signing request list

Julie
•
Sep 12, 2025
Read More

Product update, Max, App, Web Console
Introducing the "Max" button for non-native tokens

Julie
•
Sep 9, 2025
Read More

Product update, Re-broadcast, App, Web Console
New "Re-broadcast" button for non-EVM transactions

Julie
•
Sep 3, 2025
Read More

Product update, dApp, DeFi, App
dApp connections now available on mobile app

Julie
•
Jul 11, 2025
Read More

Product update, UI, App
Upgraded app home page “+” menu

Julie
•
Jul 9, 2025
Read More

Product update, Batch Payment
Batch Transaction now Supports Gas Fee Configurations

Julie
•
Jun 27, 2025
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, Story
MPCVault Now Supports Story: Unlocking New Possibilities for On-Chain IP Assets

Julie
•
Jun 11, 2025
Read More

Product update, Off-ramp
Off-Ramping Now Live – Convert Stablecoins to Fiat Instantly

Julie
•
May 12, 2025
Read More

Product update, Plans, Self-serve
Self-Serve Downgrade to Free Plan

Julie
•
May 9, 2025
Read More

Tron
Tron Wallet

Eddy
•
May 6, 2025
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, Story
Now Live: MPCVault Integrates with Story

Julie
•
May 5, 2025
Read More

Product update, Transaction Policy, App
New on App — Vault Member Management & Transaction Policy View

Julie
•
May 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, Assets, App, Web Console
Adjustable Asset Approval Amounts

Julie
•
Apr 29, 2025
Read More

Product update, App
Faster Key Certificate Backup with Mnemonics

Julie
•
Apr 25, 2025
Read More

Product update, Card, App, Web Console
Top up MPCVault Card with Solana USDC

Julie
•
Apr 23, 2025
Read More

Product update, API, Developers
REST API Interface Now Available

Julie
•
Apr 19, 2025
Read More

Product update, Sonic SVM, Blockchain Integration
New Blockchain Integration: Sonic SVM

Julie
•
Apr 17, 2025
Read More

Product update, Re-simulate, App, Web Console, Developers
Re-simulate Transactions before Signing

Julie
•
Apr 10, 2025
Read More

Product update, App
View Token Details and Manage Spam Tokens on Mobile App

Julie
•
Apr 6, 2025
Read More

BTC
BTC Wallet

Eddy
•
Apr 2, 2025
Read More

Product update, Vault
Private Vaults — Enhanced Access Control

Julie
•
Mar 28, 2025
Read More

Product update, App
Automatic Transaction Refresh on Mobile App

Julie
•
Mar 15, 2025
Read More

Product update, Batch Payment, EVM
Reminder: A Note on Batch Payments

Julie
•
Mar 8, 2025
Read More

Product update, Transaction Policy
Introducing Two Transaction Policy Modes for More Flexibility

Julie
•
Mar 4, 2025
Read More

Product update, API, Wallet, Developers
A Redesigned Wallets page

Julie
•
Mar 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, Movement
Movement integration is here!

Julie
•
Feb 27, 2025
Read More

Product update, Card, App
Top Up MPCVault Card in Mobile App

Julie
•
Feb 25, 2025
Read More

Product update, Security, Solana
Accelerate Transaction & Anti-Sandwich Protection on Solana

Julie
•
Feb 21, 2025
Read More

Product update, API, Solana, Developers
Custom Transactions on Solana

Julie
•
Feb 18, 2025
Read More

Product update, UI, Web Console
Team & Policies Page Refresh

Julie
•
Feb 11, 2025
Read More

Product update, Security, Address Book, Web Console
Address Book Upgrades

Julie
•
Feb 4, 2025
Read More

Product update, Security, TON, App, Web Console
Reminder: Proper Use of the Comment Field for TON Transactions

Julie
•
Jan 24, 2025
Read More

Product update, Re-broadcast, EVM, App, Web Console
New Re-broadcast Button for EVM Transactions

Julie
•
Jan 17, 2025
Read More

Product update, Solana, dApp, Developers
Improved Transaction Performance on Solana

Julie
•
Jan 10, 2025
Read More

Product update, Free Plan
Create Up to 5 Free Organizations

Julie
•
Jan 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, Paid Plan, Subscription
Subscription Renewal Grace Period

Julie
•
Dec 28, 2024
Read More

Product update, Card, Members Limits
Unlimited Organization Members

Julie
•
Dec 20, 2024
Read More

Product update, Card
MPCVault and Rain Partner to Launch the MPCVault Card: Spend USDC Anywhere Visa is Accepted

Julie
•
Dec 10, 2024
Read More

Product update, Solana, Assets, Interest-bearing tokens
Manage Interest Bearing Tokens on Solana

Julie
•
Dec 3, 2024
Read More

Product update, Security, Dust Transactions
Auto-detect Dust Attacks

Julie
•
Nov 30, 2024
Read More

Product update, Browser Extension, dApp, Multi-chain
The MPCVault Browser Extension

Julie
•
Nov 26, 2024
Read More

Product update, Assets, Unlisted Tokens, Web Console, Developers
New Shortcut for Importing Tokens

Julie
•
Nov 20, 2024
Read More

Product update, dApp, Web Console
Manage dApp Connections

Julie
•
Nov 12, 2024
Read More

Product update, Custom EVM Chain, Web Console, Developers
Add Custom EVM Networks

Julie
•
Nov 9, 2024
Read More

Product update, Card
Launching MPCVault Card: Pay for Real World Services with Crypto

Julie
•
Nov 7, 2024
Read More

Product update, UI, App
Brand New Send Page on Mobile App

Julie
•
Nov 6, 2024
Read More

Product update, Browser Extension, RPC
Improved RPC Reliability for Browser Plugin

Julie
•
Nov 2, 2024
Read More

Alchemy
MPCVault Featured on Alchemy's List of Top MPC Wallets

Julie
•
Oct 29, 2024
Read More

Product update, Browser Extension, dApp, TON
TON Integration for Browser Plugin

Julie
•
Oct 25, 2024
Read More

Product update, UI, App
Switching between Organizations Made Easier

Julie
•
Oct 21, 2024
Read More

Product update, Solana, dApp, Developers
Multi-Transaction Support on Solana

Julie
•
Oct 17, 2024
Read More

Product update, Solana, Assets, Token-2022
Support for Solana's Token-2022 is now live

Julie
•
Oct 9, 2024
Read More

Alchemy
MPCVault Featured on Alchemy's List of Top MPC Wallets

Julie
•
Oct 8, 2024
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, TON
MPCVault Now Supports TON

Julie
•
Sep 16, 2024
Read More

Cryptography, MPC
Homomorphic Encryption and Secure Multiparty Computation (MPC)

Webster
•
Aug 28, 2024
Read More

Security, SOC 2
MPCVault renews SOC 2 Type II Certification for 2024

Julie
•
Jun 13, 2024
Read More

Security, Tron
Maximizing Your TRON Wallet: Tips for Secure and Efficient Use

Eddy
•
Feb 4, 2024
Read More

Cross-chain, Multi-chain
Cross-Chain vs. Multi-Chain: What's the Difference?

Eddy
•
Jan 30, 2024
Read More

L1, L2
Layer 1 vs. Layer 2: What's the Difference?

Eddy
•
Jan 29, 2024
Read More

NFT, Web3
What Are NFTs? Non-Fungible Tokens Explained

Eddy
•
Jan 28, 2024
Read More

Web3, DeFi
The Evolution of Finance: How Web3 is Shaping the Future of Banking

Eddy
•
Jan 26, 2024
Read More

Crypto Taxes
Cryptocurrency Taxation: Navigating the Complex World of Crypto Taxes

Eddy
•
Jan 16, 2024
Read More

Polygon, Security
The Trust Factor: Ensuring Transparency with Polygon Wallet Solutions

Eddy
•
Jan 12, 2024
Read More

Layer-2
What Is L2? Crypto Layer 2 Explained

Eddy
•
Jan 5, 2024
Read More

Aptos, Security
Aptos Wallet Security: How to Keep Your Digital Assets from Harm's Way

Eddy
•
Dec 28, 2023
Read More

Sui, Security
Choosing the Best Sui Wallet: Essential Tips for Crypto Users

Eddy
•
Dec 18, 2023
Read More

POS, POW, Blockchain
The Proof is in the Pudding: Understanding Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake

Eddy
•
Dec 16, 2023
Read More

Ethereum, Security
Stay One Step Ahead: Proven Methods to Prevent Ethereum Scams

Eddy
•
Dec 5, 2023
Read More

Ethereum, Security
Beware of Scammers: Common ETH Scams and How to Spot Them

Eddy
•
Nov 30, 2023
Read More

Smart Contract
What Are Smart Contracts on Blockchain and How Do They Work?

Eddy
•
Nov 22, 2023
Read More

Security, Best Practices, MPCVault
Securing Your Crypto Investments: Best Practices and Common Scam Techniques

Eddy
•
Nov 18, 2023
Read More

DAO, Governance, Transparency
What is a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO)? Understanding the New Era of Governance

Eddy
•
Nov 6, 2023
Read More

Stablecoins, DeFi, Payments
What Is A Stablecoin? The Safe Haven of Cryptocurrency and Its Investment Appeal

Eddy
•
Nov 3, 2023
Read More

Cross-chain, Blockchain Bridges
What is Cross-Chain?

Eddy
•
Oct 18, 2023
Read More

Multi-chain, Interoperability, Cross-chain
What is Multi-Chain?

Eddy
•
Oct 14, 2023
Read More

ICOs, STOs
ICOs vs. STOs: The Investment Opportunities and Risk Considerations

Eddy
•
Oct 5, 2023
Read More

Cryptography, MPC
Secure Multiparty Computation

Webster
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

TEE
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 1)

Eddy
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

TEE
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 3)

Eddy
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

TEE
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 2)

Eddy
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

Security
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 3)

Eddy Sang
•
Apr 7, 2023
Read More
All (91)
Product update (60)
Assets (5)
Card (6)
Security (13)
App (25)
Developers (8)
Blogs (91)

Product update, Organization accountant
Who introduced an accountant role to the organization

Julie
•
Nov 3, 2025
Read More

Product update, Transaction Policy, Whitelist Only Mode
Whitelist Transfers: restrict transactions to approved accounts

Julie
•
Nov 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, UI, App
The Liquid Glass effect is LIVE on iOS

Julie
•
Oct 27, 2025
Read More

Product update, Sui, Swap
New Sui swap and cross-chain swap options

Julie
•
Oct 20, 2025
Read More

Product update, Card
Download card transaction history via CSV

Julie
•
Oct 13, 2025
Read More

Product update, Email Notifications, Transaction Notes
Smarter email notifications: address book labels and transaction notes

Julie
•
Oct 9, 2025
Read More

Product update, Email Notifications, UX
Direct link to transaction details from email

Julie
•
Oct 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, Off-ramp, USD
Expanded transfer type for US users

Julie
•
Sep 23, 2025
Read More

Product update, Transaction Filter, App, Web Console
The new transaction filter

Julie
•
Sep 19, 2025
Read More

Product update, Assets, Mark As Spam, App
New menu in mobile app transaction details page

Julie
•
Sep 16, 2025
Read More

Product update, API, App, Web Console
Show API requests in the signing request list

Julie
•
Sep 12, 2025
Read More

Product update, Max, App, Web Console
Introducing the "Max" button for non-native tokens

Julie
•
Sep 9, 2025
Read More

Product update, Re-broadcast, App, Web Console
New "Re-broadcast" button for non-EVM transactions

Julie
•
Sep 3, 2025
Read More

Product update, dApp, DeFi, App
dApp connections now available on mobile app

Julie
•
Jul 11, 2025
Read More

Product update, UI, App
Upgraded app home page “+” menu

Julie
•
Jul 9, 2025
Read More

Product update, Batch Payment
Batch Transaction now Supports Gas Fee Configurations

Julie
•
Jun 27, 2025
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, Story
MPCVault Now Supports Story: Unlocking New Possibilities for On-Chain IP Assets

Julie
•
Jun 11, 2025
Read More

Product update, Off-ramp
Off-Ramping Now Live – Convert Stablecoins to Fiat Instantly

Julie
•
May 12, 2025
Read More

Product update, Plans, Self-serve
Self-Serve Downgrade to Free Plan

Julie
•
May 9, 2025
Read More

Tron
Tron Wallet

Eddy
•
May 6, 2025
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, Story
Now Live: MPCVault Integrates with Story

Julie
•
May 5, 2025
Read More

Product update, Transaction Policy, App
New on App — Vault Member Management & Transaction Policy View

Julie
•
May 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, Assets, App, Web Console
Adjustable Asset Approval Amounts

Julie
•
Apr 29, 2025
Read More

Product update, App
Faster Key Certificate Backup with Mnemonics

Julie
•
Apr 25, 2025
Read More

Product update, Card, App, Web Console
Top up MPCVault Card with Solana USDC

Julie
•
Apr 23, 2025
Read More

Product update, API, Developers
REST API Interface Now Available

Julie
•
Apr 19, 2025
Read More

Product update, Sonic SVM, Blockchain Integration
New Blockchain Integration: Sonic SVM

Julie
•
Apr 17, 2025
Read More

Product update, Re-simulate, App, Web Console, Developers
Re-simulate Transactions before Signing

Julie
•
Apr 10, 2025
Read More

Product update, App
View Token Details and Manage Spam Tokens on Mobile App

Julie
•
Apr 6, 2025
Read More

BTC
BTC Wallet

Eddy
•
Apr 2, 2025
Read More

Product update, Vault
Private Vaults — Enhanced Access Control

Julie
•
Mar 28, 2025
Read More

Product update, App
Automatic Transaction Refresh on Mobile App

Julie
•
Mar 15, 2025
Read More

Product update, Batch Payment, EVM
Reminder: A Note on Batch Payments

Julie
•
Mar 8, 2025
Read More

Product update, Transaction Policy
Introducing Two Transaction Policy Modes for More Flexibility

Julie
•
Mar 4, 2025
Read More

Product update, API, Wallet, Developers
A Redesigned Wallets page

Julie
•
Mar 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, Movement
Movement integration is here!

Julie
•
Feb 27, 2025
Read More

Product update, Card, App
Top Up MPCVault Card in Mobile App

Julie
•
Feb 25, 2025
Read More

Product update, Security, Solana
Accelerate Transaction & Anti-Sandwich Protection on Solana

Julie
•
Feb 21, 2025
Read More

Product update, API, Solana, Developers
Custom Transactions on Solana

Julie
•
Feb 18, 2025
Read More

Product update, UI, Web Console
Team & Policies Page Refresh

Julie
•
Feb 11, 2025
Read More

Product update, Security, Address Book, Web Console
Address Book Upgrades

Julie
•
Feb 4, 2025
Read More

Product update, Security, TON, App, Web Console
Reminder: Proper Use of the Comment Field for TON Transactions

Julie
•
Jan 24, 2025
Read More

Product update, Re-broadcast, EVM, App, Web Console
New Re-broadcast Button for EVM Transactions

Julie
•
Jan 17, 2025
Read More

Product update, Solana, dApp, Developers
Improved Transaction Performance on Solana

Julie
•
Jan 10, 2025
Read More

Product update, Free Plan
Create Up to 5 Free Organizations

Julie
•
Jan 1, 2025
Read More

Product update, Paid Plan, Subscription
Subscription Renewal Grace Period

Julie
•
Dec 28, 2024
Read More

Product update, Card, Members Limits
Unlimited Organization Members

Julie
•
Dec 20, 2024
Read More

Product update, Card
MPCVault and Rain Partner to Launch the MPCVault Card: Spend USDC Anywhere Visa is Accepted

Julie
•
Dec 10, 2024
Read More

Product update, Solana, Assets, Interest-bearing tokens
Manage Interest Bearing Tokens on Solana

Julie
•
Dec 3, 2024
Read More

Product update, Security, Dust Transactions
Auto-detect Dust Attacks

Julie
•
Nov 30, 2024
Read More

Product update, Browser Extension, dApp, Multi-chain
The MPCVault Browser Extension

Julie
•
Nov 26, 2024
Read More

Product update, Assets, Unlisted Tokens, Web Console, Developers
New Shortcut for Importing Tokens

Julie
•
Nov 20, 2024
Read More

Product update, dApp, Web Console
Manage dApp Connections

Julie
•
Nov 12, 2024
Read More

Product update, Custom EVM Chain, Web Console, Developers
Add Custom EVM Networks

Julie
•
Nov 9, 2024
Read More

Product update, Card
Launching MPCVault Card: Pay for Real World Services with Crypto

Julie
•
Nov 7, 2024
Read More

Product update, UI, App
Brand New Send Page on Mobile App

Julie
•
Nov 6, 2024
Read More

Product update, Browser Extension, RPC
Improved RPC Reliability for Browser Plugin

Julie
•
Nov 2, 2024
Read More

Alchemy
MPCVault Featured on Alchemy's List of Top MPC Wallets

Julie
•
Oct 29, 2024
Read More

Product update, Browser Extension, dApp, TON
TON Integration for Browser Plugin

Julie
•
Oct 25, 2024
Read More

Product update, UI, App
Switching between Organizations Made Easier

Julie
•
Oct 21, 2024
Read More

Product update, Solana, dApp, Developers
Multi-Transaction Support on Solana

Julie
•
Oct 17, 2024
Read More

Product update, Solana, Assets, Token-2022
Support for Solana's Token-2022 is now live

Julie
•
Oct 9, 2024
Read More

Alchemy
MPCVault Featured on Alchemy's List of Top MPC Wallets

Julie
•
Oct 8, 2024
Read More

Product update, Blockchain Integration, TON
MPCVault Now Supports TON

Julie
•
Sep 16, 2024
Read More

Cryptography, MPC
Homomorphic Encryption and Secure Multiparty Computation (MPC)

Webster
•
Aug 28, 2024
Read More

Security, SOC 2
MPCVault renews SOC 2 Type II Certification for 2024

Julie
•
Jun 13, 2024
Read More

Security, Tron
Maximizing Your TRON Wallet: Tips for Secure and Efficient Use

Eddy
•
Feb 4, 2024
Read More

Cross-chain, Multi-chain
Cross-Chain vs. Multi-Chain: What's the Difference?

Eddy
•
Jan 30, 2024
Read More

L1, L2
Layer 1 vs. Layer 2: What's the Difference?

Eddy
•
Jan 29, 2024
Read More

NFT, Web3
What Are NFTs? Non-Fungible Tokens Explained

Eddy
•
Jan 28, 2024
Read More

Web3, DeFi
The Evolution of Finance: How Web3 is Shaping the Future of Banking

Eddy
•
Jan 26, 2024
Read More

Crypto Taxes
Cryptocurrency Taxation: Navigating the Complex World of Crypto Taxes

Eddy
•
Jan 16, 2024
Read More

Polygon, Security
The Trust Factor: Ensuring Transparency with Polygon Wallet Solutions

Eddy
•
Jan 12, 2024
Read More

Layer-2
What Is L2? Crypto Layer 2 Explained

Eddy
•
Jan 5, 2024
Read More

Aptos, Security
Aptos Wallet Security: How to Keep Your Digital Assets from Harm's Way

Eddy
•
Dec 28, 2023
Read More

Sui, Security
Choosing the Best Sui Wallet: Essential Tips for Crypto Users

Eddy
•
Dec 18, 2023
Read More

POS, POW, Blockchain
The Proof is in the Pudding: Understanding Proof of Work vs. Proof of Stake

Eddy
•
Dec 16, 2023
Read More

Ethereum, Security
Stay One Step Ahead: Proven Methods to Prevent Ethereum Scams

Eddy
•
Dec 5, 2023
Read More

Ethereum, Security
Beware of Scammers: Common ETH Scams and How to Spot Them

Eddy
•
Nov 30, 2023
Read More

Smart Contract
What Are Smart Contracts on Blockchain and How Do They Work?

Eddy
•
Nov 22, 2023
Read More

Security, Best Practices, MPCVault
Securing Your Crypto Investments: Best Practices and Common Scam Techniques

Eddy
•
Nov 18, 2023
Read More

DAO, Governance, Transparency
What is a Decentralized Autonomous Organization (DAO)? Understanding the New Era of Governance

Eddy
•
Nov 6, 2023
Read More

Stablecoins, DeFi, Payments
What Is A Stablecoin? The Safe Haven of Cryptocurrency and Its Investment Appeal

Eddy
•
Nov 3, 2023
Read More

Cross-chain, Blockchain Bridges
What is Cross-Chain?

Eddy
•
Oct 18, 2023
Read More

Multi-chain, Interoperability, Cross-chain
What is Multi-Chain?

Eddy
•
Oct 14, 2023
Read More

ICOs, STOs
ICOs vs. STOs: The Investment Opportunities and Risk Considerations

Eddy
•
Oct 5, 2023
Read More

Cryptography, MPC
Secure Multiparty Computation

Webster
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

TEE
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 1)

Eddy
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

TEE
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 3)

Eddy
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

TEE
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 2)

Eddy
•
Sep 28, 2023
Read More

Security
Demystifying TEEs: A High-Level Introduction and Their Impact on Data Security (Part 3)

Eddy Sang
•
Apr 7, 2023
Read More
Upgrade your financial OS today!
530 University Ave, Ste B, Palo Alto, CA 94301
Info@mpcvault.com
MPCVault is a non-custodial cryptocurrency wallet designed for team usage. By using our services, you acknowledge and agree that you are solely responsible for the management and security of your team's private keys, passwords, and any other sensitive information required to access and control your wallet and its associated funds. Cryptocurrency investments and transactions are subject to various risks, including price volatility, regulatory changes, and dApp vulnerabilities. By using MPCVault, you acknowledge and accept these risks and agree that MPCVault is not liable for any financial losses, damages, or consequences that may result from your use of our services or your participation in cryptocurrency transactions. It is essential for users to take proper security precautions, including but not limited to creating secure passwords, backing up private keys, and following best practices for protecting sensitive information. MPCVault is not responsible for any damages, losses, or issues that may arise from user errors, negligence, or failure to follow security guidelines. MPCVault is not a financial advisor and does not provide investment advice or recommendations. Users are responsible for conducting their own research, consulting with professionals, and making informed decisions about their cryptocurrency investments and transactions.
© 2026 MPCVault, MetaLoop Inc. All rights reserved.

Upgrade your financial OS today!
530 University Ave, Ste B, Palo Alto, CA 94301
Info@mpcvault.com
MPCVault is a non-custodial cryptocurrency wallet designed for team usage. By using our services, you acknowledge and agree that you are solely responsible for the management and security of your team's private keys, passwords, and any other sensitive information required to access and control your wallet and its associated funds. Cryptocurrency investments and transactions are subject to various risks, including price volatility, regulatory changes, and dApp vulnerabilities. By using MPCVault, you acknowledge and accept these risks and agree that MPCVault is not liable for any financial losses, damages, or consequences that may result from your use of our services or your participation in cryptocurrency transactions. It is essential for users to take proper security precautions, including but not limited to creating secure passwords, backing up private keys, and following best practices for protecting sensitive information. MPCVault is not responsible for any damages, losses, or issues that may arise from user errors, negligence, or failure to follow security guidelines. MPCVault is not a financial advisor and does not provide investment advice or recommendations. Users are responsible for conducting their own research, consulting with professionals, and making informed decisions about their cryptocurrency investments and transactions.
© 2026 MPCVault, MetaLoop Inc. All rights reserved.

Upgrade your financial OS today!
530 University Ave, Ste B, Palo Alto, CA 94301
Info@mpcvault.com
MPCVault is a non-custodial cryptocurrency wallet designed for team usage. By using our services, you acknowledge and agree that you are solely responsible for the management and security of your team's private keys, passwords, and any other sensitive information required to access and control your wallet and its associated funds. Cryptocurrency investments and transactions are subject to various risks, including price volatility, regulatory changes, and dApp vulnerabilities. By using MPCVault, you acknowledge and accept these risks and agree that MPCVault is not liable for any financial losses, damages, or consequences that may result from your use of our services or your participation in cryptocurrency transactions. It is essential for users to take proper security precautions, including but not limited to creating secure passwords, backing up private keys, and following best practices for protecting sensitive information. MPCVault is not responsible for any damages, losses, or issues that may arise from user errors, negligence, or failure to follow security guidelines. MPCVault is not a financial advisor and does not provide investment advice or recommendations. Users are responsible for conducting their own research, consulting with professionals, and making informed decisions about their cryptocurrency investments and transactions.
© 2026 MPCVault, MetaLoop Inc. All rights reserved.




